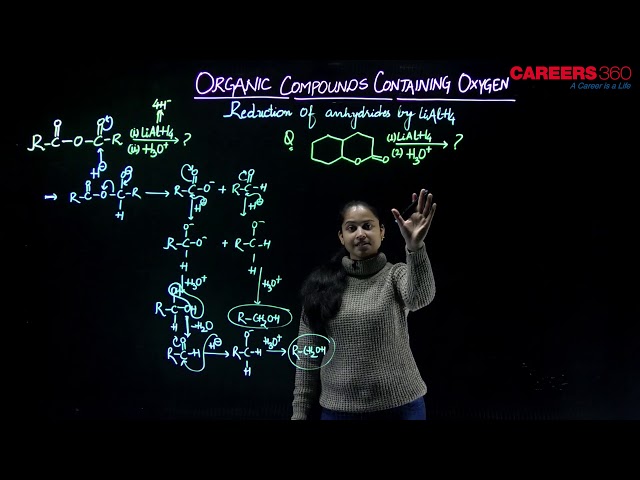Preparation of Alcohols MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Grignard Reagent - 1, Reduction by LiAlH4 and NaBH4 is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
42 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
In the following sequence of reactions
, the end product (C) is
The order of reactivity of phenyl magnesium bromide (PhMgBr) with the following compounds


NEET 2026: Exam Centres List | Free NEET Coaching & Study Material
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
When is reduced with
the compound obtained will be
The increasing order of the reactivity of the following with LiAlH4 is :
Concepts Covered - 4
All three types of monohydric alcohols can be prepared by the use of Grignard reagents. Grignard reagents form addition compounds by nucleophile attack with aldehydes and ketones which on hydrolysis with dilute acid yields alcohol.
Mechanism


For example:

Alcohols are produced by the reaction of Grignard reagents with aldehydes and ketones. The first step of the reaction is the nucleophilic addition of Grignard reagent to the carbonyl group to form an adduct. Hydrolysis of the adduct yields alcohol.
Mechanism

Anhydrides are formed by heating of two (-COOH) groups to remove (H2O) molecule. Aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and derivatives on reduction yield alcohols. A number of reducing agents link Zn/HCl, Na/C2H5OH, LiAlH4 or NaBH4 can be used for this purpose. These derivatives are reduced by nascent hydrogen into corresponding alcohols.
Some examples include,
NaBH4 can only reduce keto groups. But LiAlH4 can reduce even anhydrides and esters. LiAlH4 is a very good reducing agent because (Al) atom present in ir is more covalent than (B) atom in NaBH4. Therefore, Al has more tendency to gain the electrons, thus, it will try to keep the electrons to itself and hence H- will go in a particular manner. Thus, LiAlH4 is better reducing agent than NaBH4.
Mechanism
The mechanism for LiAlH4 occurs in the following steps:
- Deprotonation

- Nucleophilic attack by the hydride ion

- Nucleophilic attack by the hydride ion

- Leaving group removal

- Alkoxide is protonated

Some examples include:


Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"