Weightlessness MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
7 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
The rotation of the earth having radius about its axis speeds up to a value such that a man at a latitude angle
feels weightlessness. The duration of the day in such a case is:
The enzyme responsible for this reaction is
The weight of an astronaut in an orbiting artificial satellite around Earth is
Concepts Covered - 1
There are basically three cases of weightlessness -
-
When objects fall freely under gravity -
When a man is in a free-falling lift, then he will feel the weightlessness.
2. When a satellite revolves in its orbit around the Earth -
Because of this, the astronauts will feel weightlessness in the satellite.
3. When bodies are at null points in outer space -
As we go up from the earth’s surface the gravitational pull of the earth decreases and the gravitational pull of the moon increases. There is a point when both the gravitational force will be equal and opposite, that null the weight of the body and we feel weightlessness.
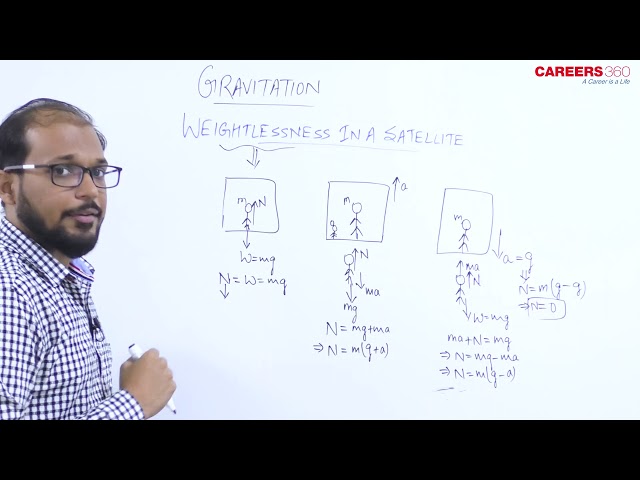
Weightlessness in a Satellite.
The acceleration of the satellite is $\frac{G M}{r^2}$ towards the center of the earth.
Let us suppose a body of mass $m$ placed on a surface inside the satellite moving around the earth.
Then force on the body is -
(i) The gravitational pull of earth $=\frac{G M m}{r^2}$
(ii) The reaction by the surface $=R$
By Newton's law $\frac{G m M}{r^2}-R=m a$
$$
\frac{G m M}{r^2}-R=m\left(\frac{G M}{r^2}\right) \quad \therefore \quad R=0
$$
As the reaction becomes 0.
And from the Laws of motion, we know that the reaction on a body will give its weight.
So, the body will feel weightlessness in the satellite.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"