X-rays MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
9 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
X-rays of wavelength are scattered from a target. The wavelength of the X-rays scattered through
is:
A material whose absorption edge is
is irradiated with
-rays. The maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons that are emitted from
-shell is
The x-Ray emission line of tungsten occurs at
. The energy difference between k and L levels in these atoms is about -
The shortest wavelength of X-rays emitted by an X-ray tube operating at :
Directions: Study the following bar chart carefully and answer the questions given beside. Given bar graph shows the number of students who passed in B.E. final year from six different colleges.

Students passed from colleges U, T, P and Q together is how much more than that of college S and R together?
Concepts Covered - 1
X-rays-
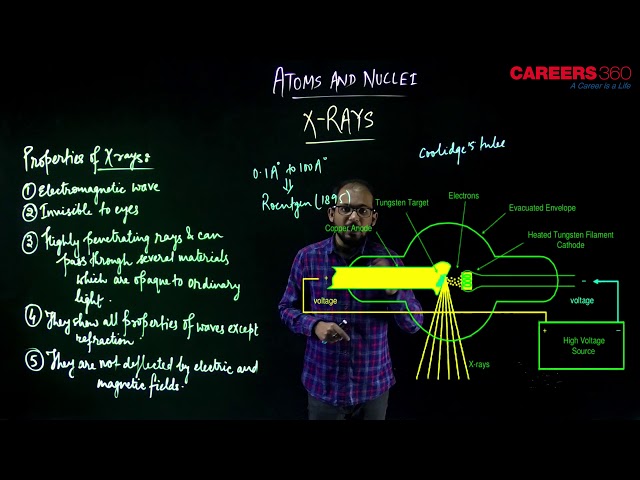
X-rays are highly energetic radiations with very short wavelengths. Their wavelength is even shorter than the ultraviolet radiations and varies between 0.03 and 3 nanometers and some x-rays are as small as a single atom of many elements. But now question arrise that how X-rays was discovered, Actually X-rays were discovered by Roentgen, who found that a discharge tube(Coolidge's tube), operating at low pressure and high voltage, emitted a radiation that caused a flouroscent in the neighborhood to glow brightly. This indicate that some unkown radiation were responsible for flouro-scence. Since the name of these rays was unkown so it is named as X-rays.
Properties of X-rays -
-
They pass through materials more or less unchanged
-
They cannot be refracted
-
Electric and magnetic fields do not have any effect on these rays
-
These radiations ionize the surrounding air by discharging electrified bodies
-
They have short wavelength varying between 0.1 A° to 1 A°.
-
They are produced when a metal anode is bombarded by very high energy electrons.
-
They do not require any medium for propagation
-
X-rays cannot be focused on a single point
-
These radiations cannot be heard or smelt
-
They travel in a straight line in free space
-
They cause photoelectric emission.
-
Intensity of X – rays depends on number of electrons hitting the target.
Application of X-rays -
- Medical Science - They are used for medical purposes to detect the breakage in human bones.
- Security - They are used as a scanner to scan the luggage of passengers in airports, rail terminals, and other places.
- Astronomy - It is emitted by celestial objects and are studied to understand the environment.
- Industry - It is widely used to detect the defects in the welds.
- Restoration - They are used to restore old paintings.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"