- Engineering and Architecture
- Management and Business Administration
- Medicine and Allied Sciences
- Law
- Animation and Design
- Media, Mass Communication and Journalism
- Finance & Accounts
- Computer Application and IT
- Pharmacy
- Hospitality and Tourism
- Competition
- School
- Study Abroad
- Arts, Commerce & Sciences
- Learn
- Online Courses and Certifications
- Home
- Study Material
- Difference Between Sympathetic And Parasympathetic Nervous System MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
13 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
How do parasympathetic neural signals affect the working of the heart?
Concepts Covered - 2
Sympathetic & Parasympathetic Nervous System
Sympathetic Neural System & Parasympathetic Neural System
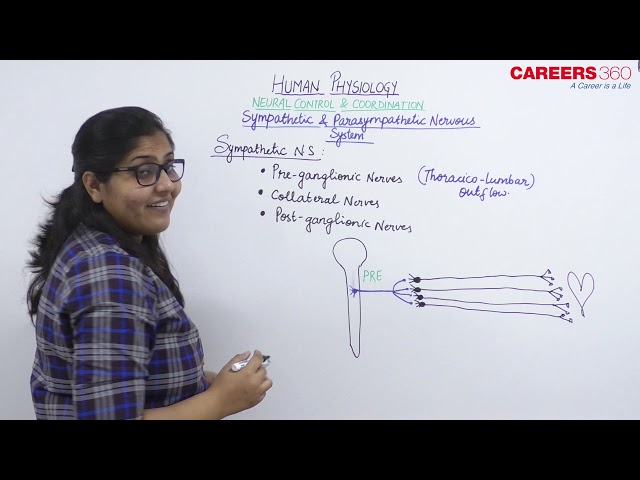
Sympathetic Neural System:
- The sympathetic neural system can be simplified into the following components:
Preganglionic fibres
Collateral Ganglia
Postganglionic fibres
- Preganglionic fibres are the axons of the neurons that are present in the spinal cord.
- Most preganglionic fibers of the sympathetic division arise from the middle, or thoracic-lumbar portion (T1 to L3) of the spinal cord
- Thus Sympathetic is also termed as Thoraco-Lumbar outflow
- The preganglionic fibres almost immediately terminate in ganglia that lie near the cord. Therefore, in this division, the preganglionic fiber is short.
- There are three collateral ganglia situated in the abdominal cavity.
- Post ganglionic fibres make contact with the organs and are longer.
- Preganglionic nerve fibres are cholinergic (filled with acetylcholine).
- Post ganglionic nerve, fibres are adrenergic (filled with noradrenaline) except sweat gland which have cholinergic postganglionic nerve fibres.
Parasympathetic Neural System:
- The preganglionic nerve fibres arise from cranial nerves 3, 7, 9, 10 and sacrum. Thus it is termed as Cranio-sacral outflow
- Preganglionic nerve fibres are longer than postganglionic nerve fibres.
- Both pre and post ganglionic nerve fiber are cholinergic.
Comparison Between Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Neural System
Comparison Between Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Neural System
| Structure | Sympathetic | Parasympathetic |
| Eye (Pupil) | Dilation | Constriction |
| Nasal mucosa | mucus reduction | Mucus increased |
| Salivary glands | Saliva reduction | Saliva increased |
| Heart | Rate reduced | Rate increased |
| Arteries | Constriction | Dilation |
| Lung | Bronchial muscle relaxation | Bronchial muscle contraction |
| Gastrointestinal tract | Decreased motility | Increased motility |
| Liver | Conversion of glycogen to glucose increased | Glycogen synthesis |
| Kidney | Decreased urine | Increased urine |
| Bladder | Contraction of sphincter | Relaxation of sphincter |
| Sweat glands | Sweat | No change |
Study other Related Concepts
Difference Between Sympathetic And Parasympathetic Nervous System Current Topic
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"

Books
Reference Books
Sympathetic & Parasympathetic Nervous System
Elementary Biology Vol 1
Page No. : 207 U5
Line : 31
Comparison Between Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Neural System
Elementary Biology Vol 1
Page No. : U5 210
Line : 5
Clear your Basics with NCERT
E-books & Sample Papers
Get Answer to all your questions
Explore on Careers360
JEE Main
RPVT
Colleges By Branches
Colleges By Exam
Colleges By Branch
Colleges By Exams
Colleges By Ownership
Colleges By State
Colleges By Exams
Colleges By Degree
Colleges by State
Colleges by City
Colleges by State
Universities by Branches
By State
Colleges by City
Colleges by State
By State
BE/B.Tech
Diploma
MBA Specialization Colleges
Student Community: Where Questions Find Answers