Phylum Aschelminthes MCQ - NEET Practice Questions with Answers
Edited By admin | Updated on Sep 18, 2023 18:34 AM | #NEET
Quick Facts
-
Phylum Aschelminthes and Body Plan of Aschelminthes, Reproduction and Development in Aschelminthes. is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
13 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Which one of the following statements about certain given animals is correct?
Which of the following groups of animals is bilaterally 40 symmetrical and triploblastic?
Concepts Covered - 3
Phylum Aschelminthes and Body Plan of Aschelminthes
- Aschelminthes are also called Nemathelminthes or Nematodes.
- These are known as ‘roundworms’ as the cross-section of the body appears circular.
- These are triploblastic and pseudocoelomate animals. It implies that there is pseudocoelomic fluid that acts to provide hydroskeleton.
- These can be parasitic or free-living.
- They show organ system level of organization
- Ascaris (Roundworm), Wuchereria (Filaria worm), Ancylostoma (Hookworm) are the examples
Body Plan of Aschelminthes:
- The epidermis is surrounded by a thick cuticle.
- It is followed by a muscular layer.
- Between the muscular layer and gut, the pseudocoelom is present which is filled with fluid.
- The digestive tract is surrounded by gastrodermis that forms the innermost layer of the body.
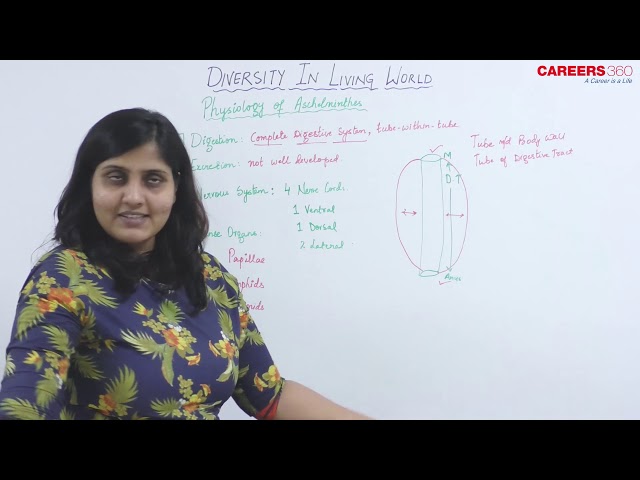
- They show a tube-within-tube type of body plan.
- They have an unsegmented body.
- The body shows tapering ends at both extremities.

Physiology of Aschelminthes
Digestion in Aschelminthes
The digestive system is complete with a distinct mouth and anus. Therefore, they have a tube-within-tube type of body plan. Digestion is extracellular. Stomach is absent.
Excretion in Aschelminthes:
- The excretory system is not well developed in nematodes.
- The nitrogenous wastes are removed through the process of diffusion via the excretory pores.
- In marine forms, the rennette glands are present below the pharynx that helps in osmoregulation.
Nervous System
- The nervous system comprises a nerve ring and nerve chords extending from it.
Reproduction and Development in Aschelminthes.
- Aschelminthes are dioecious animals, i.e., the male and female reproductive organs are present in different individuals.
- Sexual dimorphism is also observed, i.e., females are longer than the males.
- Fertilization is internal
- Development is indirect or direct
The following types of larvae are seen in different roundworms:
- Filariform larva - hookworm
- Microfilaria larva - Wuchereria
- Rhabditiform larva - Ascaris
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"