Transmission of Impulse: At Chemical Synapse MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Transmission of Impulse: At Chemical Synapse is considered one the most difficult concept.
-
26 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
The chemicals which regulate synaptic transmission at chemical synapses are called
The neurotransmitter that controls mood and induces sleep is
Which of the following is not secondary messenger?
NEET 2026: Application Form Link | Exam Centres List | How to Fill Form
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
The membrane or Ionic Theory of Nerve Impulse was proposed by
During resting state, the gate of channel is
Concepts Covered - 2
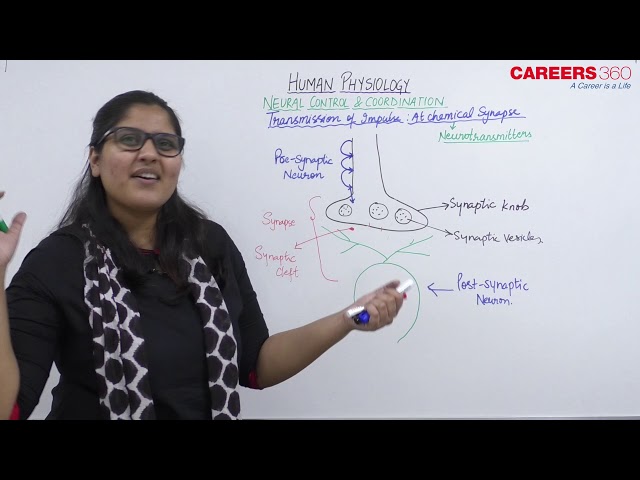
Transmission of Impulses: At Chemical Synapse
- Transmission across a chemical synapse is carried out by neurotransmitters, which are stored in synaptic vesicles in the axon terminals.
- When nerve impulses travelling along an axon reach an axon terminal, channels for calcium ions (Ca2+) open, and calcium enters the terminal.
- This sudden rise in Ca2+ stimulates synaptic vesicles to merge with the presynaptic membrane, and neurotransmitter molecules are released into the synaptic cleft.
- They diffuse across the cleft to the postsynaptic membrane, where they bind with specific receptor proteins.
- Depending on the type of neurotransmitter and the type of receptor, the response of the postsynaptic neuron can be toward excitation or toward inhibition.
- After excitatory neurotransmitters combine with a receptor, a sodium ion channel opens, and Na+ enters the neuron.

- Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that controls mood and induces sleep
- Endorphine is a neuropeptide which acts as a natural analgesic
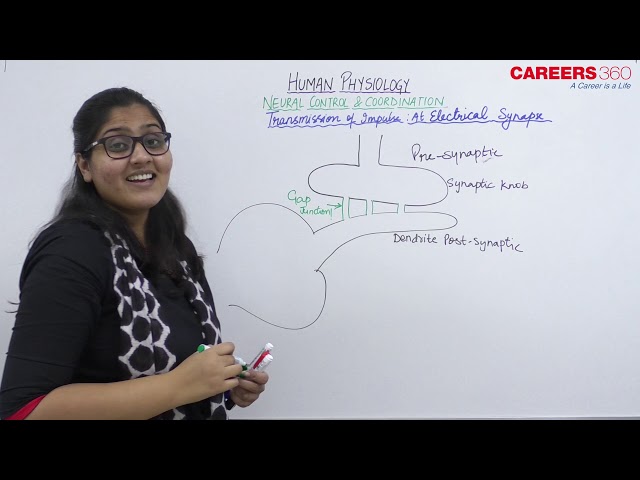
Transmission of Impulses: At Electrical Synapse
- At electrical synapses, there is continuity between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes of the neurons.
- This continuity is due to the gap junctions.
- Hence, there is a minimal synaptic delay due to direct flow of ions from one neuron to another through gap junctions.
- These are relatively rare and are found in the cardiac muscles, smooth muscles of the intestine and epithelial cells of the lens.

Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"