Tubular Reabsorption MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
21 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Out of the following excretory materials, the ones which are not reabsorbed include
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
The ascending limb of the loop of Henle is permeable to
NEET 2026: Application Form Link | Exam Centres List | How to Fill Form
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
Concepts Covered - 3
- A comparison of the volume of the filtrate formed per day (180 litres per day) with that of the urine released (1.5 litres), suggest that nearly 99 percent of the filtrate has to be reabsorbed by the renal tubules.
- This process is called reabsorption.
- This process involves both passive and active transport across the tubular epithelium.
Tubular Reabsorption in PCT:
- About 65% of the reabsorption occurs in the PCT.
- Glucose, amino acids, vitamins, hormones, sodium, potassium, chlorides, phosphates, bicarbonates, much of water and urea from the filtrate are absorbed.
- Sulphates and creatinine are not reabsorbed.
- Sodium and potassium are reabsorbed by the primary active transport.
- Glucose and amino acids are reabsorbed by the secondary active transport.
- Water is reabsorbed by osmosis.
Reabsorption in Descending Loop of Henle:
- As the filtrate moves down the descending loop of Henle, water is reabsorbed due to an increase in the osmolarity of the interstitial fluid.
- Solutes are not absorbed.
- The filtrate becomes hypertonic to blood plasma.
Reabsorption in Ascending Loop of Henle:
- This segment is impermeable to water and permeable to potassium, chlorine and sodium.
- Hence, potassium, chlorine and sodium are reabsorbed and the filtrate becomes hypotonic.
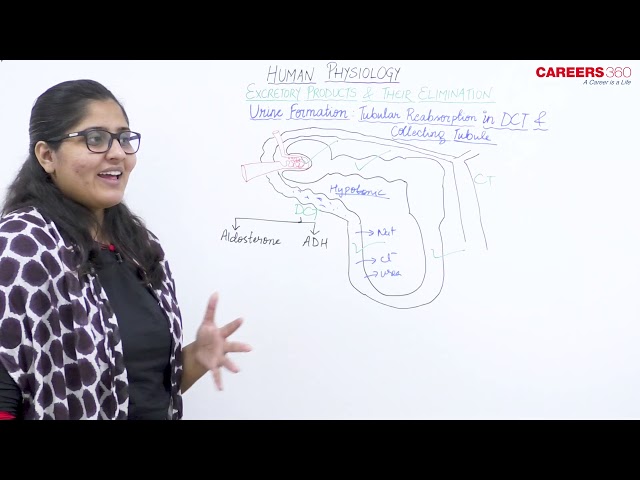
Tubular Reabsorption in DCT:
- Active reabsorption of sodium ions occurs under the influence of aldosterone.
- Chloride ions are reabsorbed under the influence of ADH.
Tubular Reabsorption in Collecting Duct:
- Water is reabsorbed due to which the filtrate becomes highly concentrated.
- Collecting duct is majorly influenced by the ADH and is permeable to water.
- Therefore, water is greatly reabsorbed here.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"