Oogenesis MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
28 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Select the incorrect statement
In human females, meiosis-II is not completed until ?
Match Column I with Column II and select the correct option using the codes given below:
|
Column I |
Column II |
|
a. Mons pubis |
(i) Embryo formation |
|
b. Antrum |
(ii) Sperm |
|
c. Trophectoderm |
iii) Female external genitalia |
|
d. Nebenkern |
(iv) Graafian follicle |
Codes :
a b c d
NEET 2026: Application Form Link | Exam Centres List | How to Fill Form
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
The Second maturation division of the mammalian ovum occurs
Concepts Covered - 1
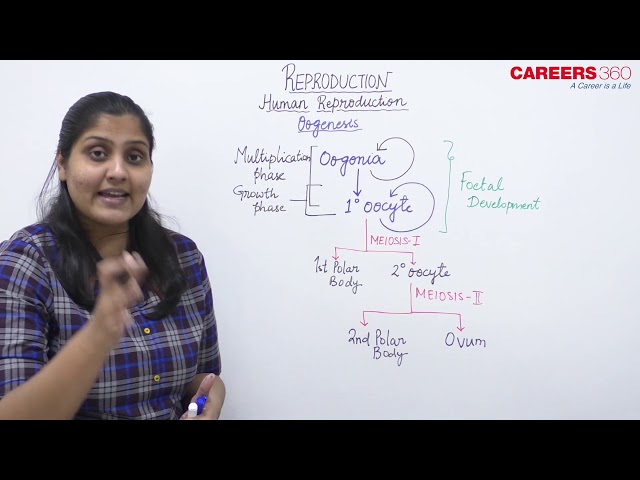
- The process of formation of a mature female gamete or ovum is called oogenesis.
- It consists of three phases:
- Multiplication phase
- Growth phase
- Maturation phase
Multiplication Phase:
- The primordial germinal cells divide repeatedly to form the oogonia.
- The oogonia multiply by the mitotic divisions and form the primary oocytes which pass through the growth phase.
Growth Phase:
- The growth phase of the oogenesis is comparatively longer than the growth phase of spermatogenesis.
- In the growth phase, the size of the primary oocyte increases enormously.
- In the primary oocyte, a large amount of fats and proteins becomes accumulated in the form of yolk and due to its heavyweight (or gravity), it is usually concentrated towards the lower portion of the egg forming the vegetative pole.
- The portion of the cytoplasm containing the egg pro-nucleus remains often separated from the yolk and occurs towards the upper side of the egg forming the animal pole.
- The cytoplasm of the oocyte becomes rich in RNA, DNA, ATP and enzymes.
- Mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, etc., become concentrated in the cytoplasm of the oocyte.
- During the growth phase, tremendous changes also occur in the nucleus of the primary oocyte.
- The nucleus becomes large due to the increased amount of the nucleoplasm and is called a germinal vesicle.
Maturation Phase:
- The maturation phase is accompanied by meiotic division.
- The meiotic division of the primary oocyte differs greatly from the meiotic division of the spermatocyte.
- Hereafter the meiotic division of the nucleus, the cytoplasm of the oocyte divides unequally to form a single large-sized haploid egg and three small haploid polar bodies or polocytes at the end.
- First meiotic division:
- After the karyokinesis, the unequal cytokinesis occurs and a small haploid polar body or polocyte and a large haploid secondary oocyte or ootid are formed.
- Second meiotic division:
- The haploid secondary oocyte and first polocyte pass through the second meiotic division.
- Due to the second meiotic division, the secondary oocyte forms a mature egg and a second polocyte.
- By the second meiotic division, the first polocyte also divides into two secondary polocytes.
- These polocytes ooze out from the egg and degenerate while the haploid egg cell becomes ready for fertilisation.
- First meiotic division:

Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"