Pistil and Megasporangium MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Edited By admin | Updated on Sep 18, 2023 18:34 AM | #NEET
Quick Facts
-
The Pistil & Megasporangium is considered one the most difficult concept.
-
15 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
The embryo sac of an Angiosperm is made up of
The ovule of an angiosperm is technically equivalent to
Concepts Covered - 1
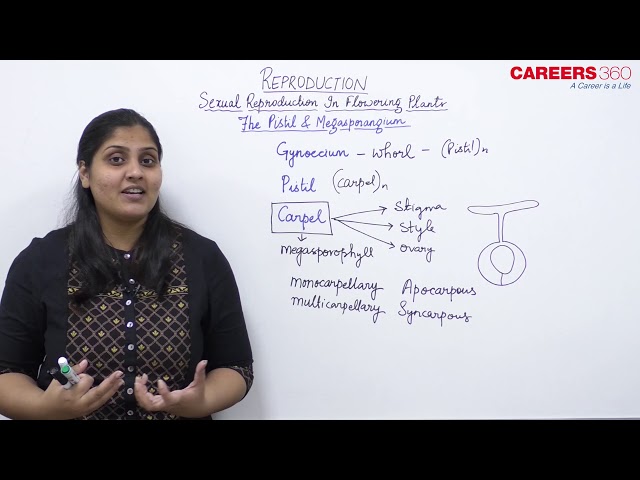
The Pistil & Megasporangium
- The gynoecium represents the female reproductive part of a flower.
- The gynoecium may consist of a single carpel (monocarpellary) or may have more than one carpel (multicarpellary).
- When there are more than one, the pistils may be fused together (syncarpous) or maybe free (apocarpous).
- Each pistil has three parts:
- stigma
- style
- ovary
- The stigma serves as a landing platform for pollen grains.
- The style is the elongated slender part beneath the stigma.
- The basal bulged part of the pistil is the ovary.
- Inside the ovary is the ovarian cavity (locule).
- The placenta is located inside the ovarian cavity.
- Arising from the placenta are the megasporangia, commonly called ovules.
- The number of ovules in an ovary may be one (wheat, paddy, mango) to many (papaya, watermelon, orchids).
Megasporangium or Ovule:
- The ovule is a small structure attached to the placenta by means of a stalk called funicle.
- The body of the ovule fuses with funicle in the region called hilum.
- Thus, hilum represents the junction between ovule and funicle.
- Each ovule has one or two protective envelopes called integuments.
- Integuments encircle the nucellus except at the tip where a small opening called the micropyle is organised.
- Opposite the micropylar end, is the chalaza, representing the basal part of the ovule.
- Enclosed within the integuments is a mass of cells called the nucellus.
- Cells of the nucellus have abundant reserve food materials.
- Located in the nucellus is the embryo sac or female gametophyte.
- An ovule generally has a single embryo sac formed from a megaspore.

- Depending on the configuration and orientation of the body of the ovule in relation to funiculus, there are six types of ovules:
- Orthotropous: erect
- Anatropous: inverted
- Hemitropous: half inverted
- Campylotropous: the body of the ovule is curved
- Amphitropous: both the body and embryo sac curved
- Circinotropous: funiculus coiled around the ovule

Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"