Placenta MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Edited By admin | Updated on Sep 18, 2023 18:34 AM | #NEET
Quick Facts
-
16 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Which one of the following is not the function of the placenta? It:
Concepts Covered - 2
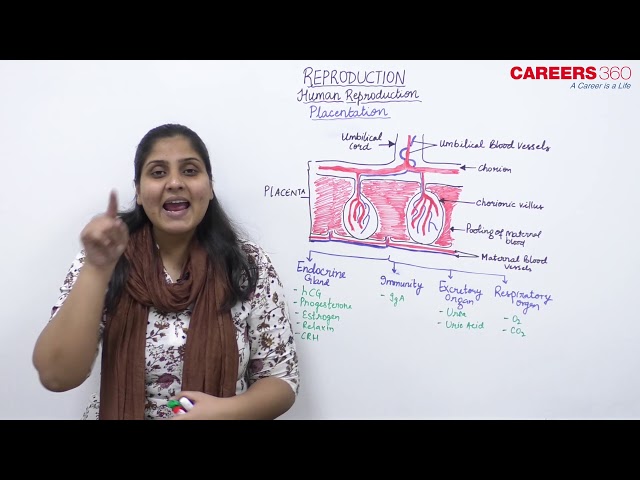
Placentation
- After implantation, finger-like projections appear on the trophoblast called the chorionic villi which are surrounded by the uterine tissue and maternal blood.
- The chorionic villi and uterine tissue become interdigitated with each other and jointly form a structural and functional unit between developing embryo (foetus) and maternal body called the placenta.
- The placenta facilitates the supply of oxygen and nutrients to the embryo and also removal of carbon dioxide and excretory/waste materials produced by the embryo.
- The placenta is connected to the embryo through an umbilical cord which helps in the transport of substances to and from the embryo.
- Placenta also acts as an endocrine tissue and produces several hormones like human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), human placental lactogen (hPL), estrogens, progestogens, etc.
- In the later phase of pregnancy, a hormone called relaxin is also secreted by the ovary.
- The hCG, hPL and relaxin are produced in women during pregnancy.
- In addition, during pregnancy the levels of other hormones like estrogens, progestogens, cortisol, prolactin, thyroxine, etc. are increased several folds in the maternal blood.
- Increased production of these hormones is essential for supporting the fetal growth, metabolic changes in the mother and maintenance of pregnancy.

Types of Mammalian Placenta
- Types of placenta according to the nature of the foetal membranes taking part in the formation of the placenta:
- Chorio-vitelline or “Yolk-sac” placenta-
- It is a primitive type of placenta found in some of the marsupials. E.g., Opossum and Kangaroo.
- In this type of placenta, the allantois remains comparatively tiny and never makes fusion with the chorion, while the yolk sac becomes very huge and combines broadly with the chorion.
- Chorio-allantoic placenta-
- In chorio-allantoic placenta, the yolk sac remains undeveloped.
- The fusion found between the uterine wall and the embryo is lined by chorion and allantois.
- Since the placenta is formed of chorion and allantois, it is termed as chorio-allantoic placenta. E.g., Parameles, Dasyurus.
- Chorionic placenta-
- The chorionic placenta is formed of a thickened layer of chorion containing sinuses filled with maternal blood.
- Chorionic type of placenta is found in human beings.
- The portion of the trophoblast which is nearer to the embryo is known as cytotrophoblast.
- The more external lying part of the trophoblast is called syncytiotrophoblast as it is a syncytium of irregular strands with interstices in between.
- Chorio-vitelline or “Yolk-sac” placenta-
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"