Degree of Dissociation MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
16 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
If the equilibrium constant for
is K, the equilibrium constant for
will be
200Ml of $\mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g})$ effuse from a Porous container in 200 sec .75 Ml of unknowns gas effuse under the same condition of temperature and pressure in 225sec. Calculates vapour density of unknown gas?
Concepts Covered - 2
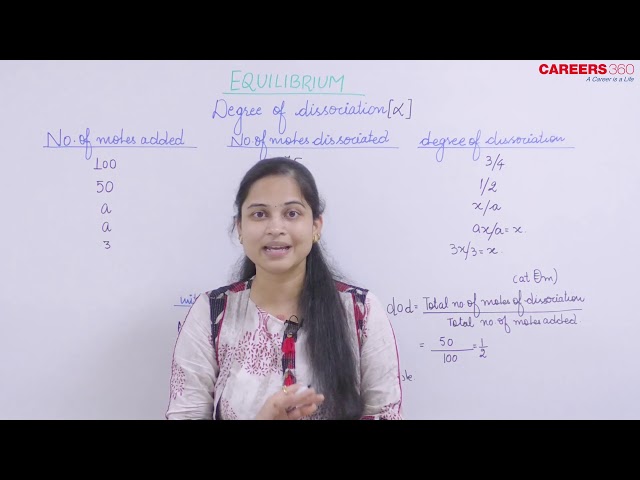
Degree of dissociation: It is the extent to which an electrolyte gets dissociated in a solvent. It is shown by 𝛂.
Degree of dissociation(𝛂) depends on the following factors:
- Nature of solute and solvent: For strong electrolytes, 𝛂 is more than that for weak electrolytes.
- 𝛂 ∝ Dielectric constant of solvent
That is, greater the dielectric constant of a solvent more will be ionization of electrolyte in it. - The degree of dissociation of weak electrolyte ∝ Dilution that is 𝛂 is maximum at infinite dilution.
- 𝛂 ∝ 1/Concentration
- 𝛂 ∝ Temperature
In equilibrium, observed molar mass or average molar mass of the reactant is the total mass of the mixture divided by the total number of moles.
Initially: 1 0
Equil: 1 - 𝛂 n𝛂
In the equilibrium system, the observed molar mass of the reactant is always different than the actual mass. Thus, when reaction is reversible, then observed mass vary. In a chemical reaction, some amount of this reactant gets convert into product, thus observed mass is different than actual mass.
For example:
In this reaction, original molar mass of N2O4 = 92g/mol. But thee observed molar mass at equilibrium is 80g/mol. The observed molar mass is less than original molar mass as during the reaction some amount of N2O4 is converted into NO2.
Vapour Density
Similarly, observed density of the substance is different than the actual density.
Thus, we know:
Vapour density = Molar mass/2
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"