Dihydrogen MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Preparation of Dihydrogen is considered one the most difficult concept.
-
Uses of Hydrogen is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
66 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
$\mathrm{Zn}+2 \mathrm{NaOH} \rightarrow A+B$
A could be :
Reaction between following pairs will produce hydrogen except :
Which of the following easily reacts with water producing hydrogen ?
NEET 2026: Exam Centres List | Free NEET Coaching & Study Material
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
Some statements about heavy water are given below:
(a) Heavy water is used as a moderator in nuclear reactors.
(b) Heavy water is more associated than ordinary water.
(c) Heavy water is more effective solvent than ordinary water.
Which of the above statements are correct?
In which reaction hydrogen is acting as an oxidant?
Concepts Covered - 0
Preparation of Hydrogen: There are a number of methods for preparing dihydrogen from metals and metal hydrides.
- Laborartory Method
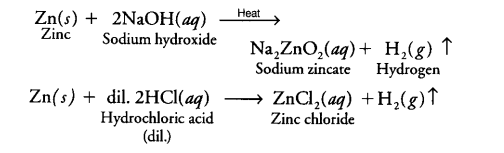
- It is usually prepared by the reaction of granulated zinc with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Zn + 2H+ → Zn2+ + H2 - It can also be prepared by the reaction of zinc with aqueous alkali.
Zn + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 + H2
- It is usually prepared by the reaction of granulated zinc with dilute hydrochloric acid.
- Commercial preparation method
- The electrolysis of acidified water using platinum electrodes gives hydrogen.
Cathode Reaction
Anode Reaction
Hydrogen gas is formed at the cathode while oxygen is formed at the anode. -
It is obtained as a byproduct in the manufacture of sodium hydroxide and chlorine by the electrolysis of brine solution. During electrolysis, the reactions that take place are:
-
- High purity (>99.95%) dihydrogen is obtained by electrolyzing warm aqueous barium hydroxide solution between nickel electrodes.
-
By the reaction of Zn with aqueous alkali : Hydrogen can also be prepared by the reaction of zinc with aqueous alkali.
-
Water Gas : Reaction of steam on hydrocarbons or coke at high temperatures in the presence of catalyst yields hydrogen.
The mixture of CO and H2 is called water gas. As this mixture of CO and H2 is used for the synthesis of methanol and a number of hydrocarbons, it is also called synthesis gas or 'syngas'.
The process of producing 'syngas' from coal is called 'coal gasification'.
-
Water Gas Shift Reaction : The production of dihydrogen can be increased by reacting carbon monoxide of syngas mixtures with steam in the presence of iron chromate as catalyst.
This is called water-gas shift reaction.
- The electrolysis of acidified water using platinum electrodes gives hydrogen.
Physical Properties of Hydrogen: Dihydrogen is a colourless, odourless, tasteless, combustible gas. It is lighter than air and insoluble in water.
The list of physical of Hydrogen and its isotopes are mentioned in the table below. Please have a look at it.

H-H bond Enthalpy : The H–H bond dissociation enthalpy is the highest for a single bond between two atoms of any element. It is because of this factor that the dissociation of dihydrogen into its atoms is only ~0.081% around 2000K which increases to 95.5% at 5000K. Also, it is relatively inert at room temperature due to the high H–H bond enthalpy.
Chemical Properties of Dihydrogen: Dihydrogen accomplishes reactions by
(i) loss of the only electron to give H+
(ii) gain of an electron to form H–
(iii) sharing electrons to form a single covalent bond.
The chemistry of dihydrogen can be illustrated by the following reactions:
- Reaction with halogens: It reacts with halogens, X2 to give hydrogen halides, HX.
- Reaction with dinitrogen: With dinitrogen it forms ammonia.
This is the method for the manufacture of ammonia by the Haber process.
- Reaction with dioxygen: It reacts with dioxygen to form water. The reaction is highly exothermic.
-
Reactions with metals: With many metals it combines at a high temperature to yield the corresponding hydrides
-
Hydrogen reacts with many organic compounds in the presence of catalysts to give useful hydrogenated products of commercial importance. For example :
- Hydrogenation of vegetable oils using nickel as catalyst gives edible fats (margarine and vanaspati ghee)
- Hydroformylation of olefins yields aldehydes which further undergo reduction to give alcohols.
The various uses of dihydrogen are as follows:
- The largest single use of dihydrogen is in the synthesis of ammonia which is used in the manufacture of nitric acid and nitrogenous fertilizers.
- Dihydrogen is used in the manufacture of vanaspati fat by the hydrogenation of polyunsaturated vegetable oils like soybean, cotton seeds etc.
- It is used in the manufacture of bulk organic chemicals, particularly methanol.
- It is widely used for the manufacture of metal hydrides.
- It is used for the preparation of hydrogen chloride, a highly useful chemical.
- In metallurgical processes, it is used to reduce heavy metal oxides to metals.
- It is used as a rocket fuel in space research.
- Dihydrogen is used in fuel cells for generating electrical energy. It has many advantages over the conventional fossil fuels and electric power.
Ortho and Para hydrogens:
In a molecule of hydrogen when the spin of both H-atoms is in the same direction, they are known as ortho hydrogen.
In a molecule of hydrogen when the spin of both H-atoms is in the opposite direction, they are known as para hydrogen.

"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"

