Electromagnetic Spectrum MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Electromagnetic spectrum is considered one the most difficult concept.
-
44 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
For sky wave propagation, the radio waves must have a frequency range in between :
Ionosphere layer of atmosphere is part of the
The condition under which a microwave oven heats a food item containing water molecules most efficiently is
NEET 2026: Application Form Link | Exam Centres List | How to Fill Form
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
The decreasing order of wavelength of infrared, microwave, ultraviolet and gamma rays is
What is the range of frequency (in KHz) for ultrasonic wave?
Concepts Covered - 1
Electromagnetic spectrum-
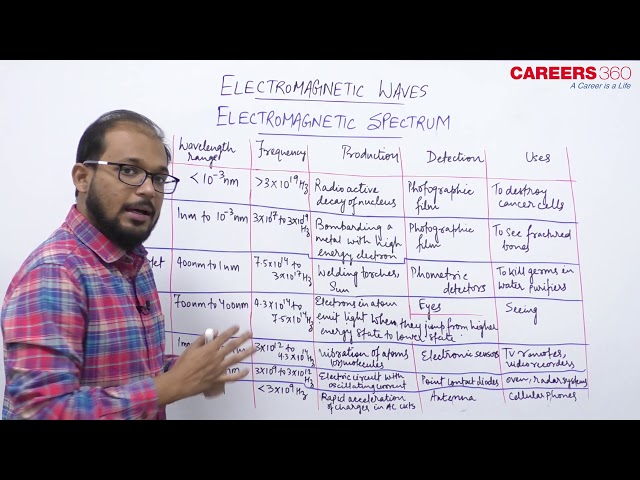
When we see our surroundings, we see only visible range of electromagnetic waves. So, the only familiar electromagnetic waves were the visible light waves. But, we now know that, electromagnetic waves include visible light waves, X-rays, gamma rays, radio waves, microwaves, ultraviolet and infrared waves. The classification of EM waves according to frequency is the electromagnetic spectrum is shown in the figure given below.

Now we will discuss all these EM waves one by one with the help of following table -

Earth's atmosphere -
(i) Troposphere : It is thermal classification of the atmosphere. In the thermosphere, temperature increases with altitude. Lowest region in the earth's atmosphere. It goes up to 17 Km.
(ii) Stratosphere: It extends between 17-50 Km above the earth surface. Ozone layer is located in the stratosphere.
(iii) Mesosphere : It is characterized by temperatures that quickly decreases with increasing height. It extends between 50-80 Km.
(iv) Ionosphere : It starts at about 75 Km and goes up to 650 Km. It contains ions and free electrons. Aurora occurs in Ionosphere.
(v) Ozone layer - It absorbs most of the ultraviolet rays emitted by the sun.
(vi) Kennelly Heaviside layer lies at about 110km from the earth's surface. In this layer concentration of electron is very high.
(vii) Exosphere - The outermost layer of earth's atmosphere. (640 Km - 1280 Km)
Point to remember -
1. Polarisation in EM wave - For an EM wave, the direction of polarisation is taken to be the direction of the electric field.
2. Wavelength of EM Wave -
$$
\begin{gathered}
\lambda=\frac{\lambda_o}{\mu} \\
\lambda_o=\text { Wavelength in vacuum } \\
\mu=\text { Refractive index of medium (Detail analysis will be }
\end{gathered}
$$
studied in Optics)
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"