Vascular Tissue System MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Vascular Tissue System is considered one the most difficult concept.
-
10 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Some vascular bundles are described as open because these
Vascular bundles in monocotyledons are considered closed because:
Concepts Covered - 1
Vascular Tissue System
- The vascular tissue system is made up of the complex tissues of xylem and phloem.
- Xylem and phloem together are referred to as vascular bundles.
- During the primary growth, the vascular bundles originate from the procambium.
- During the secondary growth, the vascular bundles originate from the vascular cambium or secondary meristem.
- In the primary plant body, the phloem differentiate from the periphery to centre (centripetal).
- In the primary plant body, xylem shows the following differentiation pattern:
- Exarch (centripetal) in root
- Endarch (centrifugal) in stem
- Mesarch (both centrifugal and centripetal) in fern rhizome



ELEMENTS OF PRIMARY VASCULAR BUNDLES IN DICOT STEM:
- The primary vascular bundles of a dicot stem consists of the following three elements
- Primary Xylem - It contains protoxylem and metaxylem
- Primary Phloem - It contains protophloem and metaphloem
- Fascicular or Intrafascicular Cambium - It is present between the xylem and phloem in the vascular bundles of stems in dicots and gymnosperms. It is a part of primary meristem.
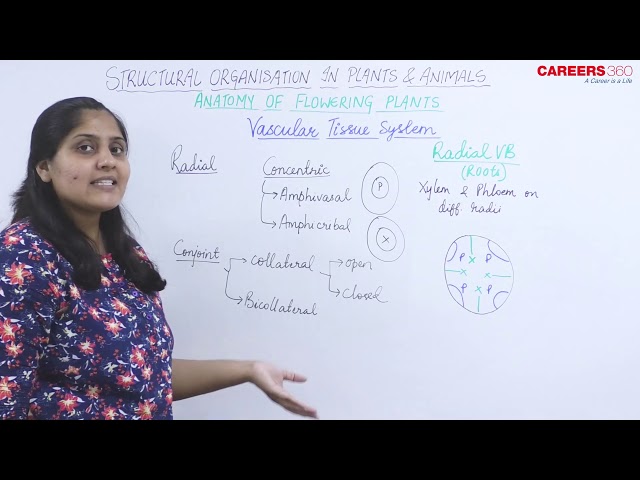
TYPES OF VASCULAR BUNDLES:
Open Vascular Bundles: When the fascicular cambium is present between the xylem and phloem. Present in dicot stems and gymnosperm stems.
Closed Vascular Bundles: When there is no fascicular cambium in between the xylem and phloem. Present in monocot stems.
Radial Vascular Bundles: When xylem and phloem are present on the different radii in the anternate fashion. It is seen in roots. It is the most primitive type of vascular bundles.
Conjoint VASCULAR BUNDLES: When xylem and phloem are present side by side on the same radius.
Conjoint Collateral Vascular Bundles: When xylem and phloem are present on the same radius and phloem is external to the xylem. These can be closed or open.
Conjoint Bicollateral Vascular Bundles: When xylem and phloem are present on the same radius but phloem is present in two patches, that is, both internal and external to the xylem. These are always open. It is the feature of family Cucurbitaceae.
Concentric Vascular Bundles: When one complex tissue completely surrounds the other complex tissue. These are always closed.
Amphivasal or Leptocentric Vascular Bundles: When xylem surrounds the phloem.
Amphicribal Or Hadrocentric Vascular Bundles: When phloem surrounds the xylem.

Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"