Root System MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
11 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
The apex of the root is protected by the
Which of the following is said to have endogenous origin?
Adventitious roots can arise from
NEET 2026: Application Form Link | Exam Centres List | How to Fill Form
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
Concepts Covered - 2
The Root System and Its Types
- The roots arise from the direct elongation of the radicle in the majority of the angiosperms.
- Roots are positively geotropic, positively hydrotropic and negatively phototropic.
- It is non-green and is not differentiated into nodes and internodes.
- The direct elongation of the radicle produces primary root which grows inside the soil.
- This primary root then bears lateral roots called secondary roots, tertiary roots etc.

Types of Root System:
1. Tap Root System: The primary root along with its lateral branches forms the tap root system. For example, mustard.

2. Fibrous Root System: In monocot plants, the primary root is short-lived and is soon replaced by a large number of roots that originate from the base of the stem. These are called fibrous roots.

3. Adventitious Root System: In some plants like grasses, banyan tree, Monstera, etc. the roots arise from parts of the plant other than the radicle. These are called adventitious roots.
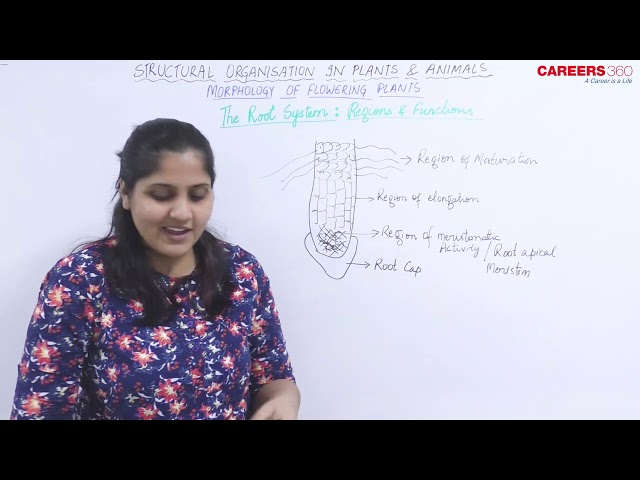
The four main regions of the roots are as follows:
1. Root cap: It is a thimble-like structure which protects the apex of the root from injuries as the root grows through the soil. It is also called the calyptra.
2. Region of meristematic activity: This region lies a few millimetres above the root cap. The cells of this region are thin-walled and have a dense protoplasm. They divide actively and add new cells.
3. Region of elongation: The cells of this region undergo elongation and enlargement. So, this region is responsible for the growth of the root.
4. Region of maturation: This region is made up of the cells that have differentiated and matured. From this region, some of the epidermal cells form very fine and delicate thread-like structures called the root hairs. Because of this, this region is also called the piliferous region.

Functions of the Root:
- Absorption of water and minerals from the soil
- Providing anchorage to the plant parts
- Storage of the reserve food material
- Synthesis of plant growth regulators
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"