Anatomy of the Human Heart NEET MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
44 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
In arteries
The tricuspid valve is present in
Concepts Covered - 4
Introduction to Human Heart
- The human circulatory system consists of a muscular heart and blood vessels associated with it.
- The heart is situated in the space of the thoracic cavity called mediastinum present between two lungs.
- It is mesodermal in origin and is slightly tilted to the left side of the body
- The average size of an adult human heart is about 12 cm.
- It gets fully developed between the age of 17-20 years
- The weight of the heart is 0.45% of the bodyweight i.e. 280-340 gms in males and 230-280 gms in females.
The external structure of the heart
- The human heart is externally covered by a double-walled membranous covering called pericardium.
- The pericardium is made up of an inner visceral and an outer parietal membrane separated by a narrow space, the pericardial cavity, filled with pericardial fluid.
- The pericardial fluid acts as a shock absorber allowing free movements of the heart
Grooves (Sulci)
- The human heart is four-chambered with a distinct transverse groove called atrioventricular groove or coronary sulcus that divides it into a smaller anterior atrial part and a posterior ventricular part
- The left and right atria are separated externally by a shallow vertical interatrial groove.
- Two grooves marking the boundary between right and left ventricles are anterior interventricular and posterior interventricular sulcus.
- Two major arterial trunks i.e. pulmonary arch and aortic arch, along with two major venous trunks i.e. superior and inferior vena cava are also seen in intimate association with heart
The internal structure of the human heart- Heart wall & Structure of atria
- The wall of the heart is made up of the following three layers from outside to inside
- Epicardium- It is the outermost layer made up of simple squamous epithelium
- Myocardium- It is the middle layer made up of cardiac muscles are striated but involuntary. It is the thickest layer
- Endocardium- Innermost layer made up of simple squamous epithelium
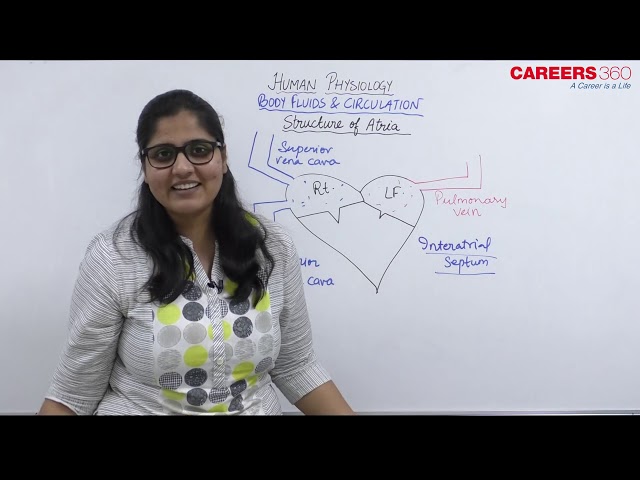
Structure of atria of the heart:
- The human heart is four-chambered divided into two atria and two ventricles
Atria
- This part is vertically divisible into right and left atria having thin walls
- The left atria is smaller than the right atria
- Each atria possess an appendage called auricle which increases the surface area of atrium.
- Each atria extends behind into a swollen flap i.e. the auricular appendix.it slightly covers the ventricle of each side
- Right, and left atria are separated by means of a thin septum called the interatrial septum or interauricular septum to prevent the mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
- An oval depression called fossa ovalis is found in the right atrium of the heart, at the level of the interatrial septum.
- The fossa ovalis is the remnant of a thin fibrous sheet that covers the foramen ovale during foetal development.
- The internal lining of the atrial wall forms a network of low muscular ridges called musculi pectinati
- The superior vena cava, inferior vena cava and coronary sinus open into the right atrium
- Superior vena cava carries blood from the body’s upper region while inferior vena cava carries blood from the body’s lower region -
- Coronary sinus carries the majority of blood from the heart itself
- Right atrium receives deoxygenated blood while left atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs (through two pairs of pulmonary veins)
- Thus Atria are regarded as 'Receiving chambers'
Internal Structure of Human Heart: Ventricles
Ventricles
- Ventricles are broad, more muscular, light coloured part of the heart
- The interventricular septum separates the left and right ventricle
- The two auricles and two ventricles are separated by the auriculoventricular septum
- The walls of the ventricles are internally raised into a number of thick, muscular, column-shaped projections called columnae carneae or trabeculae carneae
- The columnae carneae divide the cavity of the ventricles into smaller spaces called fissures
- A few large muscular elevations called papillary muscles or musculi papillaires, which are two in left ventricles and three in the right ventricle are also seen
- Fine tendinous cords called chordae tendineae are found attached to the ventricular surface of the valves on one side and to the papillary muscles on the other
- Right ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs and the left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood throughout the body
- Thus Ventricles are 'Distributing Chambers'

The internal structure of the human heart- Heart valves
- In heart, to prevent the backflow of blood or to maintain unidirectional flow of blood, following specialised valves are present in heart
1. Tricuspid valve - It guards the right atrio-ventricular opening and it has three flaps. During ventricular contraction, it prevents backflow of blood from the right ventricle into the right atrium
2. Mitral valve (bicuspid valve) - The atrioventricular opening between the left atrium and the left ventricle is guarded by mitral valve or bicuspid valve. It prevents backflow from the left ventricle into the left atrium
3.Pulmonary valve ( semilunar) - It is present in the form of three half- moon shaped pockets at the base of the pulmonary trunk and aorta. These allow free and forward flow of blood, however, prevents backward flow from pulmonary trunk into right ventricle
4. Aortic valve - It is present at the initial point of aorta and prevents backflow of blood from the aorta into the left ventricle
5. Eustachian valve - It is located at the opening of superior vena cava and prevents backflow of blood from right atrium
6. Thebesian valve ( coronary valve) - This valve is present over the opening of coronary sinus and prevents backflow of blood from the right atrium
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"