Angular Momentum MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Angular Momentum is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
30 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
A particle of mass $m$ moves along line PC with velocity $\nu$ as shown. What is the angular momentum of the particle about P?

The position vector of 1 kg object is $\vec{r}=(3 \hat{\mathrm{i}}-\hat{\mathrm{j}}) \mathrm{m}$ and its velocity $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}}=(3 \hat{\mathrm{j}}+\hat{\mathrm{k}}) \mathrm{ms}^{-1}$. The magnitude of its angular momentum is $\sqrt{\mathrm{x}} \mathrm{Nm}$ where X is:
When a mass is rotating in a plane about a fixed point, its angular momentum is directed along:
NEET 2026: Application Form Link | Exam Centres List | How to Fill Form
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
A particle of mass 2 kg is on a smooth horizontal table and moves in a circular path of radius 0.6 m. The height of the table from the ground is 0.8 m. If the angular speed of the particle is 12 rad s-1, the magnitude (in kg m2s-1) of its angular momentum about a point on the ground right under the centre of the circle is :
A small mass attached to a string rotates on the frictionless table top as shown. If the tension in the string is increased by pulling the string causing the radius of the circular motion to decrease by a factor of 2, the kinetic energy of the mass will
Concepts Covered - 1
-
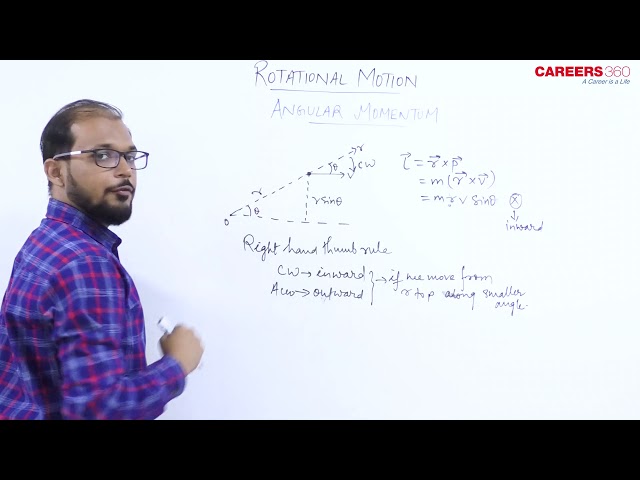
The moment of linear momentum of a body with respect to any axis of rotation is known as angular momentum. If P is the linear momentum of a particle and its position vector from the point of rotation then angular momentum is given by the vector product of linear momentum and position vector.

$\begin{aligned} \vec{L} & =\vec{r} \times \vec{P} \\ \vec{L} & =\vec{r} \times \vec{P}=\vec{r} \times(m \vec{V})=m(\vec{r} \times \vec{V}) \\ |\vec{L}| & =r p \sin \theta, \text { where } \theta \text { is the angle between } \mathrm{r} \text { and } \mathrm{p} . \\ |\vec{L}| & =m v r \sin \theta\end{aligned}$
-
Its direction is always perpendicular to the plane containing vectors r and P and with the help of the right-hand screw rule, we can find it.
Its direction will be perpendicular to the plane of rotation and along the axis of rotation
- - $L_{\max }=r * P\left(\right.$ when $\left.\theta=90^{\circ}\right)$
- - $L_{\text {min }}=0\left(\right.$ when $\left.\theta=0^0\right)$
- - SI Unit- Joule-sec or $\mathrm{kg}-\mathrm{m}^2 / \mathrm{s}$
- - Dimension- $M L^2 T^{-1}$
- - In case of circular motion

$\mathrm{As } \vec{ r} \perp \vec{v}$ and $v=\omega r$ and $I=m r^2$
$$
L=m v r=m r^2 \omega=I \omega
$$
So in vector form $\vec{L}=I \vec{\omega}$
- The net angular momentum of a system consisting of $n$ particles is equal to the vector sum of the angular momentum of each particle.
$$
\vec{L}_{n e t}=\vec{L}_1+\vec{L}_{2 \ldots \ldots}+\vec{L}_n
$$
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"