Blood vessels and their system MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
23 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Inferior vena cava
What is the name of the blood vessel that carries deoxygenated blood from the body to the heart in a frog?
Vasa recta refers to
NEET 2026: Application Form Link | Exam Centres List | How to Fill Form
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
Concepts Covered - 3
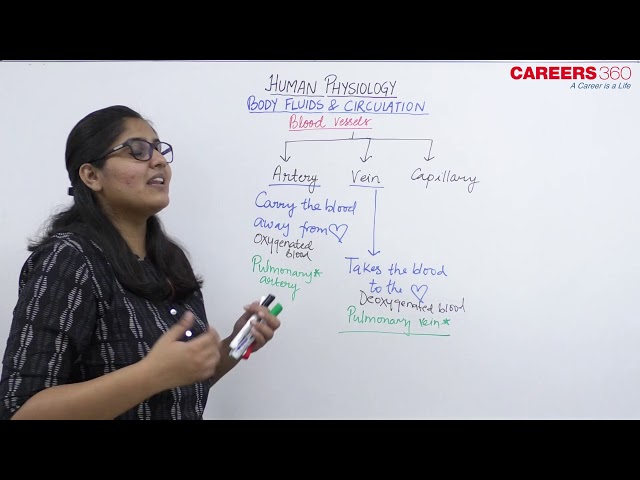
Blood vessels
- The four chambers of the heart are directly connected with the following major blood vessels
1. Systemic aorta or systemic arch - It originates from the left ventricle and distributes oxygenated blood to various body parts except lungs.
2. Pulmonary trunk or pulmonary arch - It originates from the right ventricle and gets divided into two pulmonary arteries that carry deoxygenated blood to lungs
3. Superior vena cava or precaval - It brings deoxygenated blood from head and upper parts of the body into the right atrium
4. Inferior vena cava or postcaval - It brings deoxygenated blood from the lower parts of the body into the right atrium
5. Pulmonary vein - These are four in number ( i.e. two from each lung) and bring oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium
6. Coronary veins or coronary sinus - These return deoxygenated blood from heart wall into the right atrium
Blood vessels and their system
- The study of vessels is called angiology.
- The blood vessels of a closed circulatory system are of following three types
Arteries
- These are elastic vessels that transport blood away from the heart
- The largest artery of the body is aorta
- Aorta originates from the heart and branches out into smaller arteries.
- The smallest branches are called arterioles, which further branch off into capillaries
- Arteries carry oxygenated blood except Pulmonary artery and Umbilical artery
Veins
- These are non-elastic blood vessels that transport blood to the heart.
- The smallest veins in the body are called venules.
- These receive blood from the arteries via the capillaries
- Veins carry deoxygenated blood except Pulmonary vein and Umbilical vein
Capillaries
- These are extremely small vessels that are located within the tissues of the body that transport blood from the arteries to the veins.
- Capillaries were discovered by Malpighi in 1661
- The walls of capillaries are thin and consists of only a single layer of endothelium
- The walls of capillaries help to exchange oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients and waste
Structure of wall of blood vessels
- The wall of arteries and veins consists of following three layers
1. Tunica interna- It is the innermost layer consisting of an inner endothelium of long, thin cells of squamous epithelium resting on a basement membrane along with an outer elastic membrane of yellow elastic tissue
2. Tunica media - It is the middle layer which mainly consists of smooth muscle fibres and elastic connective tissue. It is thicker in artery
3. Tunica externa - It is the outermost layer which is formed of loose connective tissue with longitudinally arranged white and yellow fibres. It is also known as tunica adventitia

Differences between arteries and veins
The differences between arteries and veins are as follows:
| Veins | Arteries |
| Move towards the heart | Move away from the heart |
| Collects blood from the body organs | Distributes blood to the body organs |
| Blood pressure in veins is low | Blood pressure in arteries is high |
| Valves are present | Valves are absent |
| Carry deoxygenated blood except for pulmonary vein and umbilical vein | Carry oxygenated blood except for pulmonary artery and umbilical artery |
| veins start from blood capillaries | Arteries end in capillaries |
| They can be seen subcutaneously | They are deep seated |
| They collapse when there is no blood in it or cut across | They do not collapse when there is no blood in it |
| Veins are further divided into venules | Arteries are divided into arterioles |
| Veins are usually flattened or collapsed with thin walls | Round and thick walled |
| Veins have large lumen | Have small lumen |
| Veins are bluish in colour | They are reddish in colour |
| Show sluggish movement of blood | Give spurty movement of blood |
| If venous wall is injured blood comes out, collects in a pool in a small area around vein | If arterial wall is injured, blood comes out like a fountain in a large area all around the artery |
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"