Charactersics and Classification of Angiosperms MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Classification of angiosperms is considered one the most difficult concept.
-
Characteristics of Angiosperms is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
23 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Angiosperms differ from gymnosperms
In angiosperms , double fertilization means
Double fertilisation is exhibited by:
NEET 2026: Application Form Link | Exam Centres List | How to Fill Form
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
Which one of the following is a correct statement?
Concepts Covered - 2
- Angiosperms are the most advanced and most dominant of all plants found.
- Angiosperms are seed-bearing plants which form flowers and fruits. It means that the seeds of angiosperms are covered inside the fruit.
- Angiosperms grow in a wide variety of habitats and occur in different forms i.e. herbs, shrubs and trees).
- The smallest angiosperm is Wolffia and the tallest is Eucalyptus (100 meters tall).
- Angiosperms are useful to us in many ways like food, fodder, fuel, clothes, medicines and several others.
- The root system is the tap root system or adventitious root system.
- Xylem has vessels and tracheids as the main conducting elements and phloem has companion cells and sieve tubes.
- Leaves show reticulate or parallel venation.
Reproduction in angiosperms:
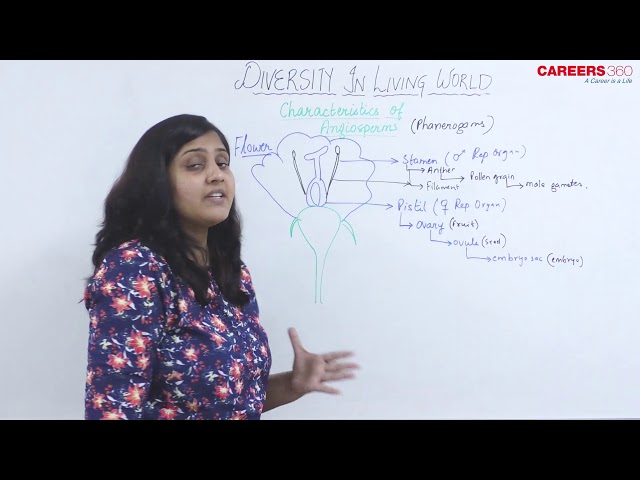
- The flowers possess stamens or androecium as male sex organ and gynoecium or carpels as female sex organs.
- Anther of the stamen has microsporangia in which microspores or pollen grains are formed from microspore mother cells upon reduction division.
- The microspores are carried to the stigma by various agents during pollination.
- The male gametophyte is three-celled.
- Gynoecium or pistil has carpels which have ovules in the ovary.
- Ovules are of various types. The most common one is anatropous ovule.
- Anatropous ovule has only one megaspore mother cell which undergoes reduction division and forms four haploid megaspores.
- One megaspore develops into the female gametophyte or embryo sac within the ovule which has 8-nuclei and 7-cells. It has an egg apparatus with three cells out of which one is egg cell and the two others are synergids. The central cell has two polar nuclei. At the posterior side, there are three antipodals.
- The pollen tube enters the ovule and eventually into its embryo sac through synergid and discharges its two male gametes.
- One of the male gametes fuses with the egg cell and forms the zygote and the second one fuses with the two polar nuclei and forms the triploid Primary Endosperm Nucleus. It is called double fertilization which is unique to angiosperms.
- Fertilisation is siphonogamous i.e. occurs with the help of pollen tube and oogamous.


Angiosperms are classified into two classes Monocotyledonae and Dicotyledonae.
Class Monocotyledonae:
- They are flowering plants characterised by the presence of a single cotyledon in the seed.
- Leave have parallel venation.
- Vascular bundles are scattered and closed.
- Flowers are trimeric.
- E.g. bananas, palms, cereals, grasses, bamboo, lilies, orchids etc.
Class Dicotyledonae:
- Flowering plants with two cotyledons in the seed
- Leaves show reticulate venation
- Vascular bundles are open and arranged in rings.
- Flowers are tetramerous or pentamerous.
- E.g. pea, rose, mustard, cotton, Acacia

Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"