Heat Transfer By Radiation MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
6 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Q amount of heat falls on a surface. 20% heat is absorbed and 35% is reflected, then the transmittance is
Concepts Covered - 1
Radiation - The process of the transfer of heat from one place to another place without any requirement of the medium is called radiation. It means that the radiation does not need any material medium to propagate.
Characteristics of Radiation -
- The process of the transfer of heat from one place to another place without heating the medium is called radiation.
- The wavelength of thermal radiation ranges from $7.8 \times 10^{-7} \mathrm{mt}$ to $4 \times 10^{-4} \mathrm{mt}$. The radiation heat transfer belongs to the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum. That is why thermal radiations are also called infrared radiations.
- Everybody whose temperature is above zero Kelvin emits thermal radiation. Practically it is not possible to reach 0 Kelvin in a finite number of steps, so every material in this universe emits radiation.
- The intensity of thermal radiation is inversely proportional to the square of the distance of the point of observation from the source $\left(I \propto \frac{1}{d^2}\right)$
- As it is an electromagnetic wave so, they follow laws of reflection, refraction, interference, diffraction, and polarisation.
- Radiation pressure - When these thermal radiations fall on a surface then exert pressure on that surface, which is called Radiation pressure.
- Radiation spectrum is obtained by quartz or rock salt prism because these materials do not have free electrons and interatomic vibrational frequency is greater than the radiation frequency, hence they do not absorb heat radiations.
- Interaction of Radiation with Matter-
When thermal radiations (Q) fall on a body, they are partly reflected, partly absorbed, and partly transmitted as shown in the below figure.
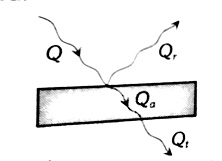
So we can write
$$
\begin{aligned}
& Q=Q_a+Q_t+Q_r \\
& \quad \frac{Q}{Q}=\frac{Q_a}{Q}+\frac{Q_t}{Q}+\frac{Q_r}{r}
\end{aligned}
$$
or $\quad 1=a+r+t$
Where
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \frac{Q_a}{Q}=a=\text { Absorptance } \\
& \frac{Q_r}{Q}=r=\text { Reflactance } \\
& \frac{Q_t}{Q}=t=\text { Transmittance }
\end{aligned}
$$
So
- If a = t = 0 and r = 1 then body is perfect reflector
-
If r = t = 0 and a = 1 then a body is a perfectly black body.
-
If, a = r = 0 and t = 1 the body is perfect transmitter
-
If $t=0 \Rightarrow r+a=1$ or $a=1-r$
i.e. good reflectors are bad absorbers.
- Prevost Theory of Heat Exchange-
- Everybody emits heat radiations at all finite temperatures (Except 0 K) as well as it absorbs radiations from the surroundings.
- The amount of heat emitted/absorbed depends on the nature of the body, the temperature of the body, and the cross-section of the body through which heat exchange is taking place.
- The exchange of energy along various bodies takes place via radiation.
- How the temperature of the body will vary will depend on the temperature of the surrounding
I. If surrounding temperature= body temperature
then $Q_{\text {emmition }}=Q_{\text {absorbed }}$
i.e the body will emit and absorb at the same rate
the temperature of the body remains constant (thermal equilibrium)
II. If surrounding temperature > body temperature
then $Q_{\text {emmition }}<Q_{\text {absorbed }}$
i.e. temperature of the body increases and it appears hotter.
III. If surrounding temperature < body temperature
then $Q_{\text {emmition }}>Q_{\text {absorbed }}$
i.e. temperature of the body decreases and consequently the body appears colder.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"














