Human Excretory System : Kidneys MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
38 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
The hormone which may increase the blood pressure is
The figure shows a human urinary system with structures labelled A to D. Select an option which correctly identifies them and gives their characteristics and/or functions.

The extended region of cortex in between the medullary pyramids forms the
NEET 2026: Application Form Link | Exam Centres List | How to Fill Form
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
In mammals, which blood vessel would normally carry the largest amount of urea?
Skin can eliminate certain substances like
Which one of the following statements regarding excretion by the human kidneys is correct?
Concepts Covered - 3
- In humans, the excretory system consists of a pair of kidneys, one pair of ureters, a urinary bladder and urethra.
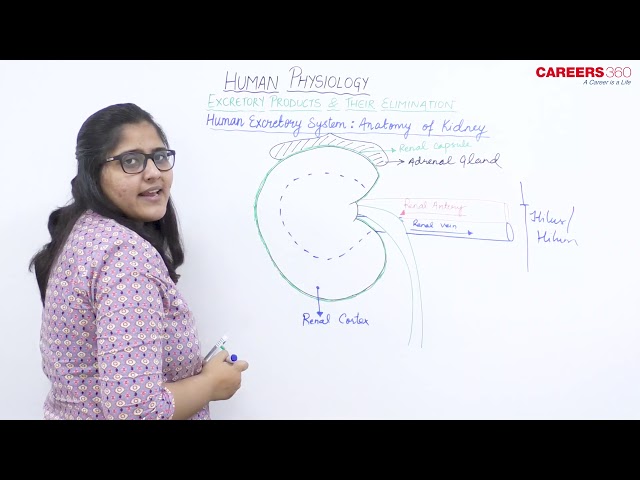
Exterior Aspects of Kidneys:
- Kidneys are reddish-brown, bean-shaped structures situated between the levels of last thoracic and third lumbar vertebra.
- Each kidney of an adult human measures 10-12 cm in length, 5-7 cm in width, 2-3 cm in thickness with an average weight of 120- 170 g.
- These are located in the retroperitoneal space between the parietal peritoneum and the posterior abdominal wall, well protected by muscle, fat, and ribs.
- The kidneys are well vascularized, receiving about 25% of the cardiac output at rest
- The left kidney is located at about the T12 to L3 vertebrae, whereas the right is lower due to slight displacement by the liver.
- Upper portions of the kidneys are somewhat protected by the eleventh and twelfth ribs
- These are directly covered by a fibrous capsule composed of dense, irregular connective tissue that helps to hold their shape and protect them.
- This capsule is covered by a shock-absorbing layer of adipose tissue called the renal fat pad.
- The renal pad is encompassed by a tough renal fascia.
- The fascia and, to a lesser extent, the overlying peritoneum serves to firmly anchor the kidneys to the posterior abdominal wall in a retroperitoneal position.
- On the superior aspect of each kidney is the adrenal gland.

- Towards the centre of the inner concave surface of the kidney is a notch called hilum through which ureter, blood vessels and nerves enter.
- A section through the kidney reveals an outer region called the renal cortex and an inner region called the medulla.
- The medulla is divided into a few conical masses (medullary pyramids) projecting into the calyces.
- Emerging from the hilum is the renal pelvis, which is formed from the major and minor calyces in the kidney.
- The cortex extends in between the medullary pyramids as renal columns called Columns of Bertini.

- The kidneys remove a number of waste products and get rid of them in the urine.
- The kidneys reabsorb nutrients from the blood and transport them to the desired place.
- They also reabsorb other products to help maintain homeostasis.
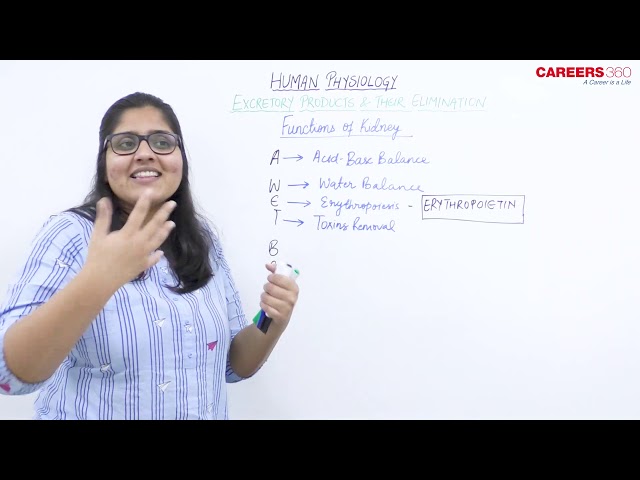
- In humans, the acceptable pH level is between 7.38 and 7.42. Below this boundary, the body enters a state of acidemia, and above it, alkalemia. The kidneys manage the pH through two processes:
- Reabsorbing and regenerating bicarbonate from urine
- Excreting hydrogen ions and fixed acids
- In response to ADH, the kidney performs osmolality regulation such as increasing urine concentration, increasing water reabsorption, reopening portions of the collecting duct that water cannot normally enter, allowing water back into the body, retaining urea in the medulla of the kidney rather than excreting it, as it draws in water.
- The kidneys release a number of important compounds, including:
- Erythropoietin: This controls erythropoiesis or the production of red blood cells. The liver also produces erythropoietin, but the kidneys are its main producers in adults.
- Renin: This helps manage the expansion of arteries and the volume of blood plasma, lymph, and interstitial fluid.
- Calcitriol: This is the hormonally active metabolite of vitamin D. It increases both the amount of calcium that the intestines can absorb and the reabsorption of phosphate in the kidney.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"