Isomers and Stereoisomers MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
8 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Anomeric carbon is
‘D’ in the name of D-Glucose signifies
The functional group on the glucose is ____ while on fructose is ____
Which statement is true regarding isomers and stereoisomers ?
Which Sugar is regarded as a C4 Epimer of Glucose?
Concepts Covered - 1
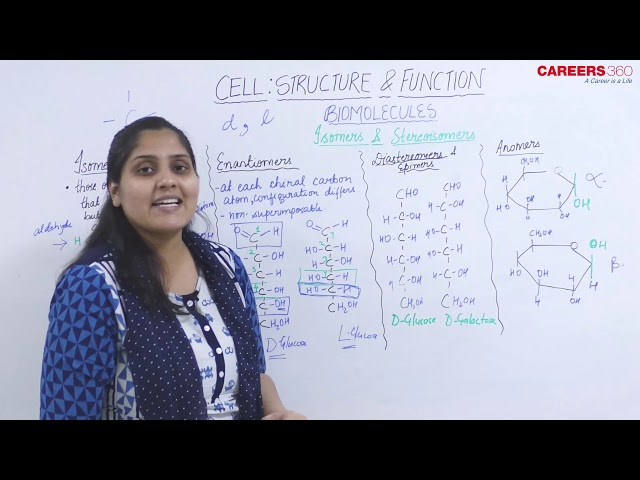
Isomers and Stereoisomers
Isomers:
- These are the organic molecules that have identical molecular formula but different arrangement of atoms.
- For example, D-Glucose and D-fructose. Both have the same molecular formula as C6H12O6. But But D-fructose has a primary alcohol at C-1 and a ketone at C-2 and D-glucose has an aldehyde at C-1 and a secondary alcohol at C-2.

Enantiomers:
- Enantiomers are those isomers that differ in their absolute configuration at each chiral carbon such that they are non-superimposable mirror images to each other.
- For example, D-Glucose and L-Glucose.

TIP: The D and L in the name of glucose refers to the direction of the -OH group of the chiral carbon which farthest from the functional group. D-Glucose has -OH placed on right side while L-Glucose has -OH placed on the left side.
Diastereomers and Epimers:
- These are the isomers that are non-superimposable on each other and are optical isomers of each other.
- Epimers are the diastereoisomers that differ in the stereochemistry at only one stereocenter.
- For example, D-Glucose and D-Galactose differ in the configuration at C-4. They are non-superimposable, and they are not mirror images of each other.

TIP: The diastereoisomers are different compounds with different names and properties while enantiomers differ only in the direction in which they rotate polarized light. They are the same compounds.
Anomers:
- When a molecule such as glucose converts to a cyclic form, it generates a new chiral centre at C-1.
- The carbon atom that generates the new chiral centre (C-1) is called the anomeric carbon.
- Anomers are the epimers that differ in configuration only at the anomeric carbon.
- For example, α-D-glucose and β-D-glucose are anomers.
- The α form has the anomeric -OH group at C-1 on the opposite side of the ring from the CH2OH group at C-5. The β form has the anomeric -OH group on the same side as the CH2OH group.

Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"