Packing Efficiency Of A Unit Cell MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Packing Efficiency is considered one the most difficult concept.
-
78 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
The vacant space in bcc lattice unit cell is :
Which of the following statements is true regarding the packing efficiency of a crystal lattice?
Percentages of free space in cubic close packed structure and in body centred packed structure are respectively
NEET 2026: Application Form Link | Exam Centres List | How to Fill Form
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
Concepts Covered - 1
Packing Efficiency in HCP and CCP Structures

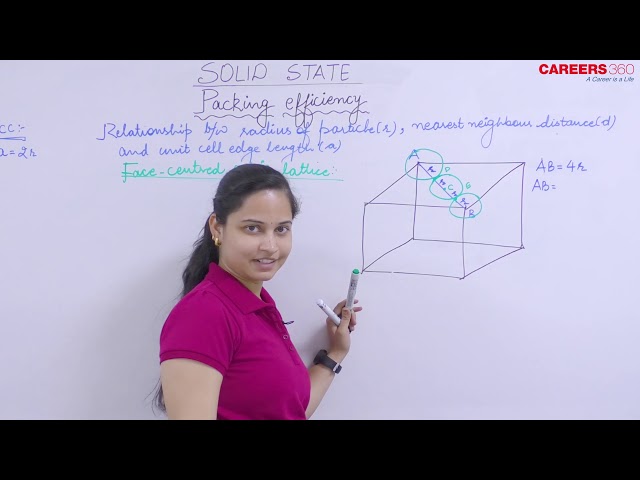
Both types of close packing (hcp and ccp) are equally efficient. Let us calculate the efficiency of packing in ccp structure. In the figure, let the unit cell edge length be 'a' and face diagonal AC = b.
In $\triangle \mathrm{ABC}$
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \mathrm{AC}^2=\mathrm{b}^2=\mathrm{BC}^2+\mathrm{AB}^2 \\
& =\mathrm{a}^2+\mathrm{a}^2=2 \mathrm{a}^2 \text { or } \\
& \mathrm{b}=\sqrt{2} \mathrm{a}
\end{aligned}
$$
If $r$ is the radius of the sphere, we find
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \mathrm{b}=4 \mathrm{r}=\sqrt{2 \mathrm{a}} \\
& \text { or } \mathrm{a}=\frac{4 \mathrm{r}}{\sqrt{2}}=2 \sqrt{2 \mathrm{r}}
\end{aligned}
$$
(We can also write, $r=\frac{a}{2 \sqrt{2}}$ )
As we know, that each unit cell in ccp structure, has effectively 4 spheres. Total volume of four spheres is equal to $4 \times(4 / 3) \pi \mathrm{r}^3$ and volume of the cube is $\mathrm{a}^3$ or $(2 \sqrt{2} \mathrm{r})^3$.
Therefore,
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \text { Packing efficiency }=\frac{\text { Volume occupied by four spheres in the unit cell } \times 100 \%}{\text { Total volume of the unit cell }} \\
& =\frac{4 \times(4 / 3) \pi r^3 \times 100}{(2 \sqrt{2})^3} \% \\
& =\frac{(16 / 3) \pi r^3 \times 100}{16 \sqrt{2} r^3}=74 \%
\end{aligned}
$$
Efficiency of Packing in Body Centred Cubic Structures

From figure, it is clear that the atom at the centre is in touch with the other two atoms diagonally arranged.
In $\triangle E F D$
$$
\mathrm{b}^2=\mathrm{a}^2+\mathrm{a}^2=2 \mathrm{a}^2
$$
$$
\mathrm{b}=\sqrt{2 \mathrm{a}}
$$
Now in $\triangle \mathrm{AFD}$
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \mathrm{c}^2=\mathrm{a}^2+\mathrm{b}^2=\mathrm{a}^2+2 \mathrm{a}^2=3 \mathrm{a}^2 \\
& \mathrm{c}=\sqrt{3} \mathrm{a}
\end{aligned}
$$
The length of the body diagonal cis equal to $4 r$, here is the radius of the sphere (atom), as all the three spheres along the diagonal touch each other.
So $\sqrt{3} a=3 r$
$$
a=\frac{4 r}{\sqrt{3}}
$$
Hence we can write, $r=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}$ a
In this type of structure, total number of atoms is 2
and their volume is $2 \times \frac{(4)}{3} \pi r^3$
Volume of the cube, $\mathrm{a}^3$ will be equal to $\frac{(4 \mathrm{r})^3}{\sqrt{3}}$ or $\mathrm{a}^3$
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \text { Therefore, Packing efficiency }=\frac{\text { Volume occupied by two spheres in the unit } \times 100 \%}{\text { Total volume of the unit cell }} \\
& =\frac{4 \times(4 / 3) \pi r^3 \times 100}{\left[(4 \sqrt{3}) r r^3\right.} \% \\
& =\frac{4 \times(4,3) \pi r^3 \times 100}{64 /(3 \sqrt{3}) r^3} \% \\
& =68 \%
\end{aligned}
$$
Coordination Number (C. No.)
- In Simple Cubic (SC): 6
- In Face Centered Cubic (FCC): 12
- In Body Centered Cubic (BCC): 8
Density of Lattice Matter (d)
It is the ratio of mass per unit cell to the total volume of a unit cell and it is found out as follows.
Here, d = Density
Z = Number of atoms
N0 = Avogadro number
a3 = Volume
a = Edge length
Here in order to find density of unit cell in cm3, m must be taken in g/mole and should be in cm.
Radius Ratio
It is the ratio of radius of an octahedral void to the radius of sphere forming the close-packed arrangement Normally ionic solids are more compact as voids are also occupied by cation (smaller in size) pattern of arrangements and type of voids both depend upon relative size (ionic size) of two ions in solid.
Example, when r+ = r- the most probable and favourable arrangement is BCC type.
With the help of relative ionic radii, it is easier to predict the most probable arrangement. This property is expressed as radio ratio.
From the value of radius ratio, it is clear that larger the radius ratio larger is the size of cation and more will be the number of anions needed to surround it, that is, more co-ordination number.
- Radius ratio for tetrahedron

- Radius ratio for octahedron

Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"