Photosynthetic Pigments - Chlorophyll, Carotenoids and Phycobilins MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Edited By admin | Updated on Sep 18, 2023 18:34 AM | #NEET
Quick Facts
-
Photosynthetic Pigments: Carotenoids and Phycobilins is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
29 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
The energy of light is contained in
The central ion in the porphyrin ring of chlorophyll is
Chromatophores take part in:
Which statement is incorrect about Phycobilins?
Concepts Covered - 2
Photosynthetic Pigments: Chlorophyll
- Pigments are substances that have the ability to absorb light at specific wavelengths
- Light is a form of electromagnetic energy that travels in waves.
- The energy of light is called Quantum energy contained in packets called photons.
- The light reflected by the pigments is the one they do not absorb
- There are three types of photosynthetic pigments:
- Chlorophyll
- Carotenoids
- Phycobilins
Chlorophyll
- It is water-insoluble but soluble in organic solvents.
- It is synthesized from the raw materials succinyl co-A, glycine, nitrogen, magnesium, and iron.
- The precursor of chlorophyll is protochlorophyll.
- Protochlorophyll lacks two hydrogen atoms, one at the 7th carbon atom and the other at the 8th carbon atom of IVth pyrrole ring.
- In the presence of sunlight, these hydrogens are added to the protochlorophyll and it is converted to chlorophyll.
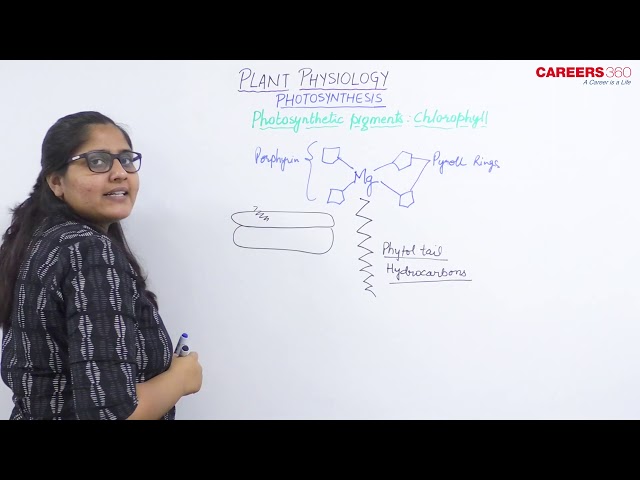
- Chlorophylls are magnesium-porphyrin compounds having a hydrophilic head and hydrophobic or lipophilic phytol tail.
- The chemical formula of the lipophilic tail is C55H39OH.
- The porphyrin ring consists of 4 pyrrole rings, a central magnesium ion, and 20A long phytol tail.
- Chlorophyll formation is a reduction process occurring in the presence of light.
- If plants are placed in the dark, they get yellowish due to a lack of chlorophyll. This is called etiolation.
- Etiolation is seen in angiosperms only.
- Gymnosperms have an enzyme called chlorophyllase which converts protochlorophyll to chlorophyll. Hence, etiolation does not occur in gymnosperms when kept in the dark.

Photosynthetic Pigments: Carotenoids and Phycobilins
Carotenoids:
- Carotenoids are plant pigments responsible for bright red, yellow, and orange hues.
- These act as shield pigments to prevent chlorophyll from photooxidation.
- These help plants absorb light energy for use in photosynthesis.
- These are water-insoluble but soluble in organic solvents.
- There are two types of carotenoids: Carotenes and Xanthophylls.
- The difference between the two groups is chemical: xanthophylls (C40H56)2) contain oxygen, while carotenes (C40H56) are hydrocarbons and do not contain oxygen.
- Also, the two absorb different wavelengths of light during a plant’s photosynthesis process, so xanthophylls are more yellow while carotenes are orange.
- The common type of carotene is beta-carotene.
- The common type of xanthophyll is lutein.
- The ratio of xanthophyll to carotene in plants is 3:1 or 2:1.
Phycobilins:
- These are water-soluble pigments.
- They contain 4 pyrrole rings but lack magnesium ions and a phytol tail.
- These occur in blue-green algae and red algae.
- There are two main types of phycobilins - phycocyanin (blue) and phycoerythrin (red)
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"