Phylum Chordata MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Edited By admin | Updated on Sep 18, 2023 18:34 AM | #NEET
Quick Facts
-
6 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Which one of the following statements is totally wrong about the occurrence of notochord, while the other three are correct?
Which of the following statements is true for the phylum Chordata?
(a) In a Urochrdata, the notochord extends from head to tail and is present throughout their life.
(b) In Vertebrata, the notochord is present during the embryonic period only
(c) The central nervous system is dorsal and hollow
(d) Chordata is divided into 3 subphyla: Hermichordata, Tunicata, and Cephalochordata
Concepts Covered - 1
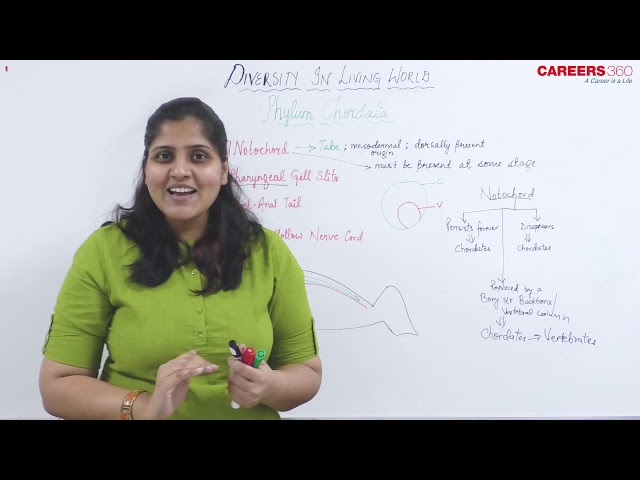
Phylum Chordata
The phylum chordata is characterized by the following:
Notochord:
- The name ‘Chordata’ is based on the presence of notochord at some stage or throughout the life cycle
- It is a rod-like structure placed dorsally between the alimentary canal and nerve cord
- It is derived from the mesoderm
- In vertebrates, it is present during the embryonic development
- It is then replaced by the vertebral column (spine) in the postnatal stage
Dorsal Hollow Nerve Cord:
- It is placed dorsally to the notochord
- It is hollow rod and is derived from the ectoderm
- It develops into the brain and spinal cord and forms the central nervous system
Pharyngeal Gill Slits:
- These are the openings present in the pharynx.
- They allow the entry and exit of water in aquatic animals.
- In vertebrate fishes, these develop into gills. In tetrapods, these are modified into tonsils and components of ears.
Post-anal Tail:
- It is the posterior elongation of the body that goes beyond the anus.
- It consists of skeletal elements and muscles.
- It helps in locomotion in fishes and in balancing in terrestrial vertebrates.
- It is reduced and non-functional in man.

Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"