Structure of Nephron and its Types MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT), Loop of Henle, Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) and Collecting Duct is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
49 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
If Henle’s loop were absent from mammalian nephron, which of the following is to be expected?
Vasa recta refer to
Bowman’s capsule is present in
NEET 2026: Application Form Link | Exam Centres List | How to Fill Form
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
The maximum amount of electrolytes and water (70 - 80 per cent) from the glomerular filtrate is reabsorbed in which part of the nephron?
Choose the correctly matched pair:
Concepts Covered - 3
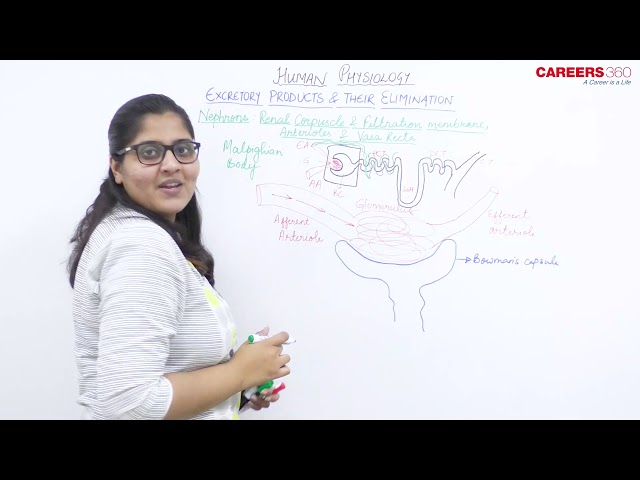
- Each kidney has nearly one million complex tubular structures called nephrons which are the functional units.
- Each nephron is supplied with a tuft of high-pressure capillaries fed by the afferent arteriole, called the glomerulus.
- The rest of the nephron consists of a continuous sophisticated tubule whose proximal end surrounds the glomerulus and is called the Bowman’s capsule.
- The glomerulus and Bowman’s capsule together form the renal corpuscle or Malpighian Body.
- After passing through the renal corpuscle, the capillaries form a second arteriole, the efferent arteriole.
- These will next form a capillary network around the more distal portions of the nephron tubule, the peritubular capillaries and vasa recta, before returning to the venous system.
- The outermost layer of the Bowman’s capsule is called the parietal layer and is made up of simple squamous epithelium.
- The visceral layer is closely associated with the glomerulus.
- The visceral layer is made up of unique cells called podocytes.
- Podocytes are highly specialized cells of the visceral layer of the glomerular capsule of the renal corpuscle of the nephron of the kidney.
- These are called podocytes because they possess foot-like projections called the pedicels.
- The space between the pedicels is called slit pores or filtration slits, through which the glomerular filtrate filters.
Filtration Membrane of Renal Corpuscle:
- Filtration membrane is the series of layers which collectively determine the pore size through which water and small dissolved solutes exit the blood plasma to become the plasma filtrate in the renal corpuscle of the nephron of the kidney; it consists of three layers:
- The endothelium of glomerulus which is perforated by small holes called the fenestrae
- The basement membrane of the glomerulus made up of a meshwork of collagen protein
- The outer layer of podocyte's (the visceral layer of the glomerular capsule)


Proximal Convoluted Tubule (PCT):
- The tubule continues further to form a highly coiled network – proximal convoluted tubule
- It is called convoluted due to its tortuous path.
- It is lined by simple cuboidal epithelium bearing brush-border of tall microvilli at the free end.
- These increase the surface area for absorption.
Loop of Henle:
- It starts at the end of the Loop of Henle.
- Its major portion lies in the medulla of the kidney.
- It consists of a descending limb and an ascending limb.
- The upper part of the descending limb is thick and made up of cuboidal epithelium.
- The lower part of the ascending limb is thin and made up of squamous epithelium.
- The ascending part of the Loop of Henle is majorly made up of thin segment.
- The thick segment of the ascending part is lined by cuboidal epithelium.
- The descending limb of Henle’s loop is permeable to water but impermeable to salts
Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT):
- It lies in the cortex of the kidney.
- It is lined by cuboidal epithelium that has few, small and irregular microvilli.
Collecting Duct:
- It is also lined by cuboidal or columnar epithelium.
- Many distal convoluted tubules combine to form the collecting duct.
- The collecting ducts combine to form still larger ducts called the duct of Bellini.
- The run through the renal papilla and merge into the ureter.
- Length of collecting duct determines the ability to concentrate its urine in mammals

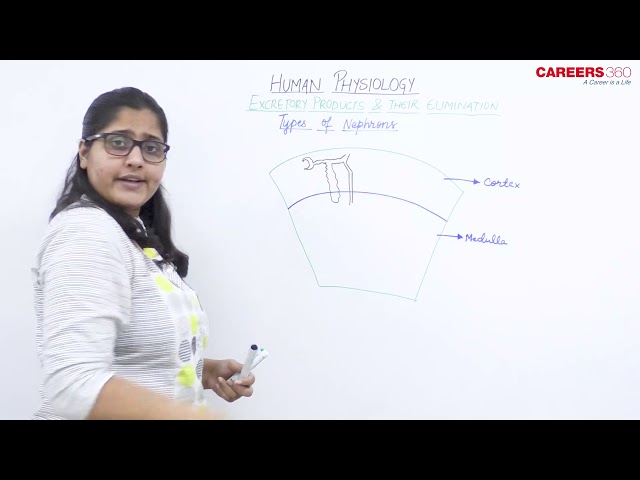
Juxtamedullary Nephrons:
- They form about 15% of the total nephrons.
- Their glomeruli are found at the junction of the cortex and medulla.
- These are larger in size and the loop of Henle are present deeper into the medulla.
- The loop of Henle is associated with vasa recta.
- They are responsible for controlling the volume of plasma when the water supply is short.
Cortical Nephrons:
- They form about 85% of the total nephrons.
- They lie in the renal cortex. The glomeruli are present in the outer cortex.
- The loop of Henle is short and extend a short distance into the medulla.
- The vasa recta are absent.

Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"