The Cytoskeleton MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Edited By admin | Updated on Sep 18, 2023 18:34 AM | #NEET
Quick Facts
-
The Cytoskeleton is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
17 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Cytoskeleton is made up of:
Which of the following is not a function of the cytoskeleton in a cell?
Concepts Covered - 1
The Cytoskeleton
The Cytoskeleton
- Cytoskeleton refers to the network of protein fibres that help in maintaining the shape of the cell and help in the movement of the cell.
- There are three types of protein fibres within cytoskeleton:
- microfilaments,
- intermediate filaments, and
- microtubules
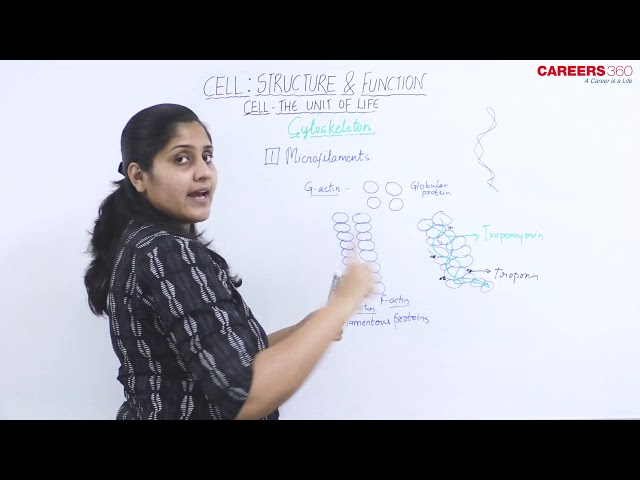
Microfilaments
- These are the narrowest fibres made up of two intertwined strands of F-actin protofilaments. They are also called actin filaments.
- F-actin protofilaments are made up of G-actin subunit.
- F-actin is the filamentous actin while G-actin is the globular actin.
- The individual strands of F-actin protofilaments are wound together with the help of tropomyosin.
- Tropomyosin is a double-stranded alpha-helical coiled-coil protein.
- It bears a protein complex, called troponin, which is interspersed along the length of the coil.
Functions of Microfilaments:
- Microfilaments provide shape and rigidity to the cells. They can depolymerize (disassemble) and reform quickly, thus enabling a cell to change its shape and move.
Intermediate Filaments
- They are called the intermediate filaments because their diameter (8 to 10 nm) is between those of microfilaments and microtubules.
- These are structural in function.
- They do not perform any role in the movement.
- They maintain the shape of the cell by bearing the tension.
- Their main function is to maintain the shape of the cell and provide tensile strength.
- These are formed through the process of polymerization.
Microtubules
- These are small hollow tubules.
- Their walls are made up of polymerised dimers of a-tubulin and B-tubulin.
- They have a diameter of 25 nm. They are the widest component of the cytoskeleton.
- They help the cell resist compression, provide a track along which vesicles move through the cell and pull replicated chromosomes to opposite ends of a dividing cell.
- Like microfilaments, microtubules can dissolve and reform quickly.

Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"