Transformers MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Transformers is considered one the most difficult concept.
-
22 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
The core of any transformer is laminated so as to
Step up transformer is used to
Step down transformer is used to
NEET 2026: Application Form Link | Exam Centres List | How to Fill Form
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
A coil is suspended in a uniform magnetic field, with the plane of the coil parallel to the magnetic lines of force. When a current is passed through the coil it starts oscillating; it is very difficult to stop. But if an aluminium plate is placed near to the coil, it stops. This is due to :
Concepts Covered - 1
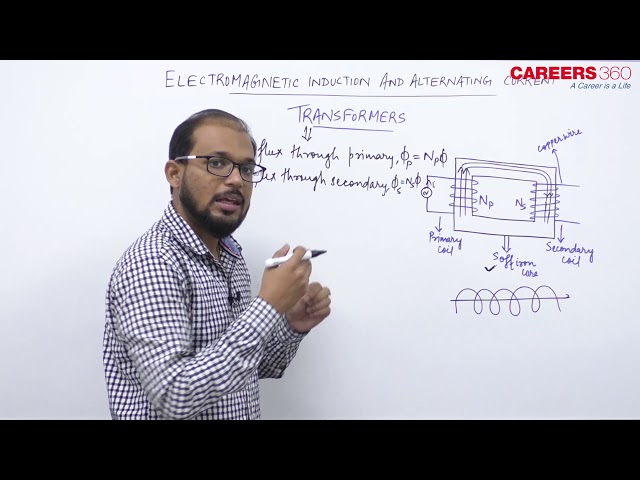
Transformers
It is a device that raises or lowers the voltage in ac circuits through mutual induction. It consists of two coils wound on the same core. The alternating current passing through the primary creates a continuously changing flux through the core. This changing flux induces an alternating emf in the secondary.

Step-up Transformer: A transformer in which the output (secondary) voltage is greater than its input (primary) voltage is called a step-up transformer.
Step-up Transformer: A transformer in which the output (secondary) voltage is less than its input (primary) voltage is called a step-down transformer
- The transformer works on ac only and never on dc.
- It can increase or decrease either voltage or current but not both simultaneously.
- Transformer does not change the frequency of input ac.
- There is no electrical connection between the winding but they are linked magnetically.
- Effective resistance between the primary and secondary winding is infinite.
- The flux per turn of each coil must be same i.e.
$$
\phi_S=\phi_P \quad-\frac{d \phi_P}{d t}=-\frac{d \phi_S}{d t}
$$
If $N_{P=\text { number of turns in primary, }} N_S=$ number of turns in secondary,
$V_P=$ applied (input) voltage to primary,
$V_S=$ Voltage across secondary (load voltage or output),
$e_{P=\text { induced emf in primary ; }}$
$e_S=$ induced emf in secondary,
$\phi_{=}$flux linked with primary as well as secondary, current in primary;
$i_{S=}$ current in secondary (or load current)
As in an ideal transformer, there is no loss of power i.e. $P_{\text {out }}=P_{\text {in so, }} V_S i_S=V_P i_P$ and $V_P \approx e_P, V_S \approx e_S$.
Hence,$$
\frac{e_S}{e_P}=\frac{N_S}{N_P}=\frac{V_S}{V_P}=\frac{i_P}{i_S}=k, \quad \mathrm{k}=\text { Transformation ratio. }
$$
Efficiency of transformer ( $\boldsymbol{\eta}$ ): Efficiency is defined as the ratio of output power and input power i.e. $\eta$.
For an ideal transformer, $P_{\text {out }}=P_{\text {in so }} \eta=100$.
For practical transformer, $P_{\text {in }}=P_{\text {out }}+P_{\text {losses. Efficiency of a practical transformer lies between } 70-90 \% \text {. }}^{\text {. }}$
So
$$
\eta=\frac{P_{\mathrm{out}}}{\left(P_{\mathrm{out}}+P_L\right)} \times 100=\frac{\left(P_{\mathrm{in}}-P_L\right)}{P_{\mathrm{in}}} \times 100
$$
Losses in transformer: In transformers, some power is always lost due to, heating effect, flux leakage eddy currents, hysteresis and humming.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"