Types Of Collision MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Types of collision is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
12 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
A block of mass 0.50 kg is moving with a speed of 2.00 ms-1 on a smooth surface. It strikes another mass of 1.00 kg and then they move together as a single body. The energy loss (in Joule) during the collision is :
Concepts Covered - 1
-
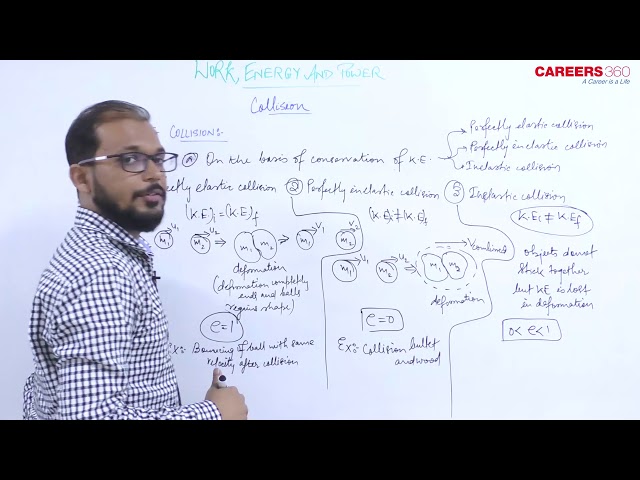
On the basis of the conservation of kinetic energy
a. Perfectly elastic collision
-
In this collision, $(K . E)_{\text {initial }}=(K . E .)_{\text {final }}$
-
Coefficient of restitution e = 1
-
Ex- Bouncing of ball with same velocity after the collision with ground.
b. Inelastic collision
-
In this collision $(K . E)_{\text {initial }} \neq(K . E .)_{\text {final }}$
-
Coefficient of restitution 0 < e < 1
-
As $(K . E)_{\text {initial }}>(K . E .)_{\text {final }}$
The loss in kinetic energy appears in other forms, such as heat, sound, etc.
Ex- Collision between two billiard balls. The majority of collisions belong to this category.
c. Perfectly inelastic collision.
-
If in a collision two bodies stick together or move with the same velocity after the collision, the collision is said to be perfectly inelastic.
-
Coefficient of restitution e = 0
-
An ex-collision between a bullet and a block of wood is an example of a perfectly inelastic collision, if after a collision the bullet remains embedded in the block, and the block and bullet move together.
-
On the basis of the direction of colliding bodies
a. Head-on or one-dimensional collision
-
In a head-on collision, the motion of colliding particles before and after the collision is along the same line.
b. Oblique collision
-
If the direction of motion of colliding particles after the collision is not along the initial line of motion of colliding particles, then the collision is called oblique.
-
Example: Collision of billiard balls.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"