Degree Of Freedom MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
14 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Directions: In this question, a word is represented by only one set of numbers as given in any one of the alternatives. The sets of numbers given in the alternatives are represented by two classes of alphabets as in the two matrices, given below. The columns and rows of Matrix (I) are numbered from 0 to 4 and that of Matrix (II) are numbered from 5 to 9. A letter from these matrices can be represented first by its row and next by its column, e.g. 'U' can be represented by 01, 12, etc., and 'L' can be represented by 56, 67, etc. Similarly, you have to identify the set for the word.
SPARE
Concepts Covered - 1
Degree of freedom-
The degree of freedom of systems is defined as the possible independent motions, systems can have.
Or
The degree of freedom of systems is defined as the number of independent coordinates required to describe the system completely.
The independent motions can be translational, rotational vibrational, or any combination of these.
So the degree of freedom is of three types :
(i) Translational degree of freedom
(ii) Rotational degree of freedom
(iii) Vibrational degree of freedom
The degree of freedom is denoted by $f$.
It is given by
$$
f=3 N-R
$$
Where
$$
\begin{aligned}
& N=\text { no. of particle } \\
& R=\text { no. of relation }
\end{aligned}
$$
- Value of degree of freedom for
1. Monoatomic gas-
A monoatomic gas can only have a translational degree of freedom.
$$
\text { l.e } f=3
$$
Example- $\mathrm{He}, \mathrm{Ne}, \mathrm{Ar}$
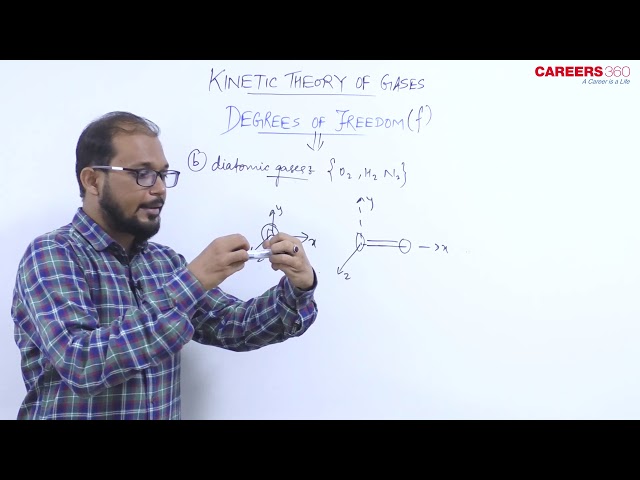
2. Diatomic gas
A diatomic gas can have three translational degrees of freedom and two rotational degrees of freedom.
..e $f=5$
Example- $\mathrm{H}_2, \mathrm{O}_2, \mathrm{~N}_2$
3. Triatomic gas
A triatomic gas can have three translational degrees of freedom and three rotational degrees of freedom.
I.e $f=6$
Example- $\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$
- Note-
The above degrees of freedom are shown at room temperature. Further at high temperatures, in the case of diatomic or polyatomic molecules,
the atoms within the molecule may also vibrate with respect to each other. In such cases, the molecule will have 2 additional degrees of freedom, due to vibrational motion. I.e One for the potential energy and one for the kinetic energy of vibration.
So A diatomic molecule that is free to vibrate (in addition to translation and rotation) will have 7 degrees of freedom.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"