Isobaric Process MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Isobaric process is considered one the most difficult concept.
-
25 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
When heat is given to a system in an isobaric process, then
If and
denote the specific heats of nitrogen per unit mass at constant pressure and constant volume respectively, then
One mole of ideal monoatomic gas is mixed with one mole of diatomic gas
. What is
for the mixture?
denotes the ratio of specific heat at constant pressure, to that at constant volume.
1 mole of a gas with is mixed with 1 mole of a gas with
, then the value of
for the resulting mixture is
Concepts Covered - 1
Isobaric Process- A Thermodynamic process in which pressure remains constant is known as the isobaric process.
In this process, V and T change keeping P constant. I.e Charle’s law is obeyed in this process
Key points in the Isobaric Process-
- Its Equation of state is given as $\frac{V}{T}=$ constant
$$
\text { І.e } \frac{V_1}{T_1}=\frac{V_2}{T_2}=\text { constant }
$$
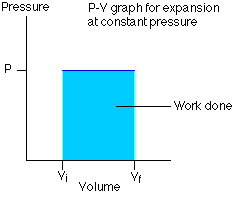
- - P-V Indicator diagram for an isobaric process. Its PV graph has slope $=0$ (i.e $\frac{d P}{d V}=0$,
The above Graph represents an isobaric expansion.
The P-V diagram for this process is a line parallel to the volume line.
- Specific heat of gas during the isobaric process is given by
$$
C_P=\left(\frac{f}{2}+1\right) R
$$
- The bulk modulus of elasticity during the isobaric process is given by
$$
K=\frac{\Delta P}{-\Delta V / V}=0
$$
- Work done in the isobaric process-
$$
\Delta W=\int_{V_i}^{V_f} P d V=P \int_{V_i}^{V_f} d V=P\left[V_f-V_i\right]
$$
Or we can write $\Delta W=P\left(V_f-V_f\right)=n R\left[T_f-T_t\right]=n R \Delta T$
- Internal energy in an isobaric process
$$
\Delta U=n C_V \Delta T=n \frac{R}{(\gamma-1)} \Delta T
$$
- Heat in an isobaric process
From FLTD $\Delta Q=\Delta U+\Delta W$
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \qquad \begin{aligned}
\Delta Q & =n \frac{R}{(\gamma-1)} \Delta T+n R \Delta T=n R \Delta T\left[\frac{1}{\gamma-1}+1\right] \\
\Rightarrow \Delta Q & =n R \Delta T \frac{\gamma}{\gamma-1}=n\left(\frac{\gamma}{\gamma-1}\right) R \Delta T=n C_p \Delta T
\end{aligned} \\
& \text { So } \Delta Q=n C_p \Delta T
\end{aligned}
$$
- Examples of the isobaric process-
1. Conversion of water into vapor phase (boiling process)
From the first law of thermodynamics
$$
\Delta Q=\Delta U+\Delta W=\Delta U_K+\Delta U_P+\Delta W
$$
since $\Delta U_K=0$ [as there is no change in temperature] and using, $\Delta Q=m L$
$$
\begin{aligned}
\Delta Q & =\Delta U_P+P\left[V_f-V_t\right] \\
\Delta U_P & =\Delta Q-P\left[V_f-V_t\right] \\
\Delta U_P & =m L-P\left[V_f-V_i\right]
\end{aligned}
$$
2. Conversion of ice into water
From FLOT $\Delta Q=\Delta U+\Delta W$ and using, $\Delta Q=m L$
we get $m L=\Delta U_P+\Delta U_K+\Delta W$
$$
m L=\Delta U_P+\Delta U_K+P\left(V_f-V_i\right)
$$
since $\Delta U_K=0$ [as there is no change in temperature]
and $\Delta W=0$ [As $V_f-V_{i \text { is negligible, I.e, when ice converts into water then changes }}$ in volume, is negligible]
Hence $\Delta U_P=m L$
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"