Refraction And Dispersion Of Light Through A Prism MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Refraction Through A Prism 1, Refraction Through A Prism 2, Dispersion Of Light 1 is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
53 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
A ray of light is incident at an angle of $60^{\circ}$ on one face of a prism of angle $30^{\circ}$. The emergent ray of light makes an angle of $30^{\circ}$ with the incident ray. The angle made by the emergent ray with the second face of the prism will be:
Concepts Covered - 4
A prism is a transparent medium whose refracting surfaces are not parallel but are inclined to each other at an angle A which is also known as angle of the prism.

The angle of deviation -It is the angle between the emergent and the incident ray.
For the above figure
and using
Note-From the above formula, we can say that if we interchange i and e then also we will get the same value of .
- The plot of

As shown in the above figure The graph is a parabola.
If we vary i between
then the value of
decreases
and the value of
increases
And when
and when
- Grazing Incidence-When i = 90°, the incident ray grazes along the surface of the prism. This is known as grazing incidence.
- Grazing Emergence- When e = 90°, the emergent ray grazes along the prism surface. This is known as grazing emergence.
This happens when the light ray strikes the second face of the prism at the critical angle for glass - air.
I.e For the prism of refractive index places in the air.
then then e = 90°
Refractive index of prism $(\mu)_{\text {in che }}$ case minimum deviation condition-
As we learned The angle of deviation $(\delta)$ for the prism is given as $\delta=i+e-A$ and from The plot of $\delta$ vs $i$ we get $i=e$ then $\delta=\delta_{\text {min }}$
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \text { i.e } \delta_{\min }=i+e-A=i+i-A=2 i-A \\
\Rightarrow & i=\frac{A+\delta_{\min }}{2}
\end{aligned}
$$

For the prism of refractive index $\mu_{\text {places in the air. }}$
For the first surface, we can write $1 * \sin i=\mu \sin r_1$
similarly For the second surface, we can write $\mu \sin r_2=1 * \operatorname{sine}$
using i=e we get $r_1=r_2$
$$
\begin{aligned}
A & =r_1+r_2=2 r_1 \\
\rightarrow r_1 & =\frac{A}{2}
\end{aligned}
$$
So $1 * \sin i=\mu \sin r_1$ will give us
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \Rightarrow 1 * \sin \left(\frac{A+\delta_{\min }}{2}\right)=\mu \sin \left(\frac{A}{2}\right) \\
\Rightarrow \mu & =\frac{\sin \left(\frac{A+\delta_{\min }}{2}\right.}{\sin \left(\frac{A}{2}\right)}
\end{aligned}
$$
- For thin films (i.e $A$ and $\delta_{\min }$ are small)
Then
$$
\sin \left(\frac{A+\delta_{\min }}{2}\right)=\frac{A+\delta_{\min }}{2}
$$
$$
\text { and } \sin \left(\frac{A}{2}\right)=\frac{A}{2}
$$
So we get
$$
\begin{gathered}
\mu=\frac{A+\delta_{\min }}{A} \\
\Rightarrow \delta_{\min }=A(\mu-1)
\end{gathered}
$$
- condition of no emergence-
i.e A ray of light incidence on a prism of angle A \& Refractive index $\mu$ will not emerge out of a prism
This will happen when $A>2 \theta_c$
where $\theta_c=$ critical angle
Dispersion of light -The splitting of white light into its constituent colors or wavelengths is called dispersion of light.
or
angular splitting of a ray of white light into a number of components and spreading in different directions is called diversion of light.
This phenomenon arises due to the fact that the refractive index varies with wavelength.
When white light is incident on the prism it will split itself into its constituent colors as shown in the below figure.
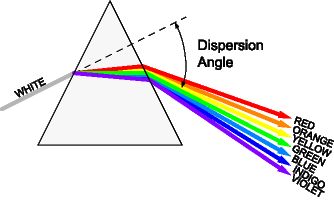
The deviation is given as $\delta=(\mu-1) A$
Since $\mu_{\text {violet }}>\mu_{\text {red }}$
So $\delta_{\text {violet }}>\delta_{\text {red }}$
- Angular dispersion ( $\theta$ )-Angular separation between extreme colors
$$
\text { i.e } \boldsymbol{\theta}=\boldsymbol{\delta}_V-\boldsymbol{\delta}_R=\left(\boldsymbol{\mu}_V-\boldsymbol{\mu}_R\right) \boldsymbol{A}
$$
It depends upon $\mu$ and A .
- Dispersive power ( $\boldsymbol{\omega}$ )- Ratio of angular dispersion to mean deviation.
$$
\omega=\frac{\delta_v-\delta_r}{\delta}
$$
where there $\delta$ is deviation of mean ray (especially yellow)
$u \operatorname{sing} \quad \delta_v=\left(\mu_v-1\right) A, \delta_r=\left(\mu_r-1\right) A$
we get $\omega=\frac{\mu_v-\mu_r}{\mu_y-1} \quad$ where $\quad \mu_y=\frac{\mu_v-\mu_r}{2}$
where
$\mu_v=$ Refractive index of violet
$\mu_r=$ Refractive index of red
$\mu_y=$ Refractive index of yellow
Condition for deviation without dispersion-
This means an achromatic combination of two prisms in which net(or) resultant dispersion is 0, but and deviation is produced as shown in the below figure.
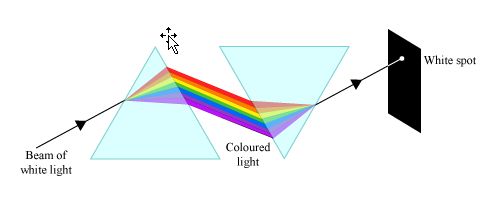
For the two prisms,
$$
\begin{gathered}
\theta_{\text {net }}=0 \Rightarrow \theta_1+\theta_2=0 \\
\left(\mu_v-\mu_r\right) A+\left(\mu_v^{\prime}-\mu_r^{\prime}\right) A^{\prime}=0 \\
\Rightarrow \quad A^{\prime}=\frac{\left(\mu_v-\mu_r\right) A}{\mu_v^{\prime}-\mu_r^{\prime}}
\end{gathered}
$$
where
$\mu_v=$ Refractive index of violet ( prism 1)
$\mu_r=$ Refractive index of red ( prism 1)
$\mu_v^{\prime}=$ Refractive index of violet ( prism 2)
$\mu_r^{\prime}=$ Refractive index of red ( prism 2)
Similarly
For the two prisms,
$$
\begin{aligned}
& \theta_{\text {net }}=0 \Rightarrow \theta_1+\theta_2=0 \\
& \omega \delta+\omega^{\prime} \delta^{\prime}=0 \\
& \Rightarrow \delta^{\prime}=-\delta \frac{\omega}{\omega^{\prime}} \\
& \Rightarrow \delta_{\text {net }}=\delta+\delta^{\prime}=\delta\left[1-\frac{\omega}{\omega^{\prime}}\right]
\end{aligned}
$$
where $\omega$ and $\omega^{\prime}$ are the dispersive powers of the two prisms and their corresponding mean deviations are $\delta$ and $\delta^{\prime}$.
Condition for Dispersion without deviation-
A combination of two prisms in which deviation produced for the mean ray by the first prism is equal and opposite to that produced
by the second prism will give a dispersion of light without deviation.
This combination of two prisms is also called a direct vision prism.
$$
\text { i.e } \delta_{\text {net }}=0 \text { while } \theta_{\text {net }} \neq 0
$$
As shown in the above figure as emergent rays from the second prism is parallel to the incident white ray of the prism 1.
this will give $\delta_{\text {net }}=0$.
For zero deviation ,
$$
\begin{array}{r}
\text { i.e } \delta_{\text {net }}=0\left(\text { i.e } \delta+\delta^{\prime}=0\right) \\
\Rightarrow \quad\left(\mu_y-1\right) A+\left(\mu_y^{\prime}-1\right) A^{\prime}=0 \\
\Rightarrow \quad A^{\prime}=\frac{\left(\mu_y-1\right) A}{\left(\mu_y^{\prime}-1\right)}
\end{array}
$$
and the Angular dispersion is given as
$$
\theta_{\mathrm{net}}=\theta_1+\theta_2=\left(\omega \delta+\omega^{\prime} \delta^{\prime}\right)=\left(\omega \delta-\omega^{\prime} \delta\right)=\theta\left(1-\frac{\omega^{\prime}}{\omega}\right)
$$
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"




