Apomixis & Polyembryony MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Edited By admin | Updated on Sep 18, 2023 18:34 AM | #NEET
Quick Facts
-
Apomixis & Polyembryony is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
18 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Polyembryony is nothing but
Concepts Covered - 1
Apomixis & Polyembryony
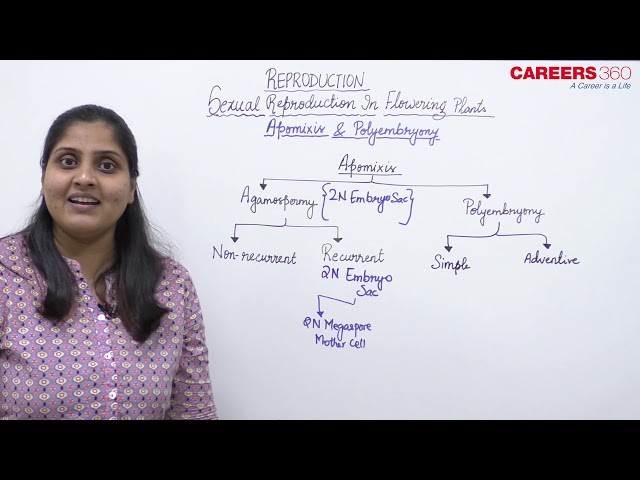
Apomixis:
- Apomixis (Gk. apo- without, mixis- mixing) is a mode of reproduction which does not involve the formation of zygote through gametic fusion.
- Hence, there is no fertilization involved.
- In plants apomixis commonly mimics sexual reproduction but produces seeds without fertilisation, e.g., some species of Asteraceae and grasses.
- It is of following types:
- Agamospermy
- Adventive embryony
Agamospermy:
- Agamospermy (Gk. a- without, gamos- marriage, sperma- seed) is the formation of seed that has an embryo formed without meiosis and syngamy.
- It is of two types, non-recurrent and recurrent.
- In non-recurrent agamospermy, the embryo is haploid. Therefore, the seed having it is non-viable.
- In recurrent agamospermy all the cells of the embryo sac are diploid.
- These can be formed:
- directly from a nucellar cell (apospory)
- Indirectly from diploid megaspore mother cell (diplospory)
- The diploid egg, as well as other diploid cells of the embryo sac, can grow into normal embryos.
- Formation of an embryo directly from a diploid egg without fertilization is called diploid parthenogenesis, e.g., Rubus, Apple, Poa.
Adventive Embryony:
- An embryo develops directly from a diploid cell other than an egg like that of nucellus and integument, e.g., Citrus, Opuntia.
- It gives rise to a condition called polyembryony or the phenomenon of having more than one embryo.
- There may be more than one egg cell in an embryo sac or more than one embryo sac in an ovule.
- All the egg cells may get fertilised.
- Synergids and antipodal cells may also form embryos.
- In gymnosperms, polyembryony can also occur due to cleavage of growing embryo.
- It is called cleavage polyembryony.
- The occurrence of polyembryony due to fertilisation of more than one egg is called simple polyembryony.
- Formation of extra embryos through sporophytic budding is called adventive polyembryony.
- Polyembryony is quite common in Onion, Groundnut, Mango, Lemon, Orange.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"