Forces MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
10 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
As shown in the figure below, the two forces are parallel and in the same direction. A pushes with 20N and B pulls with 60N. Find the net equivalent force on the box.

Concepts Covered - 1
-
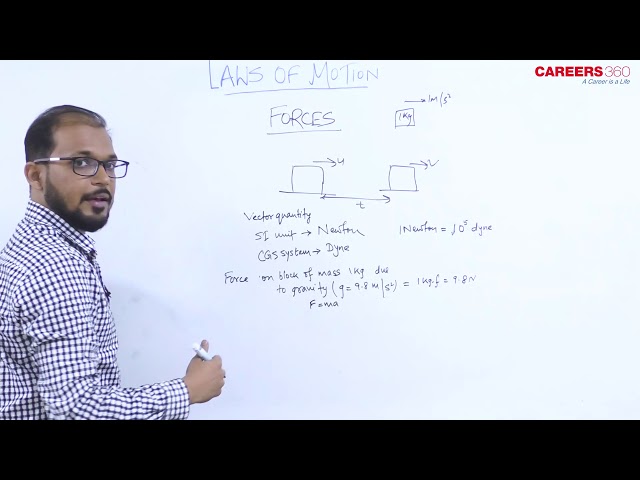
Definition- Force is defined as an effect that causes a body to change its state.
-
Force on 1 kg mass in the presence of gravity $\left(g=9.8 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^2\right)$ is 1 kg-f=9.8 N
-
Unit of force-
-
In SI unit- Newton(N)
-
In CGS- 1 dyne (1 newton = 100000 dyne)
-
1 Newton(N) is the force needed to accelerate an object with a mass of 1 kg at a rate of 1 m/s2 (1 N = 1 kg · m/s2)
2. Types of forces-
a) Contact forces-
-
Contact forces are due to direct physical contact between objects.
Types of contact forces-
- Tension
- Normal reaction
- Spring force
- Friction
b) Non-contact forces-
-
These forces act without the necessity of physical contact between objects.
-
They depend on the presence of a “field” in the region of space surrounding the body under consideration.
Types of non-contact forces-
- Gravitational force
- Electrostatic force
- Magnetic force
c) Weak forces-
-
Vanderwaal force
d) Nuclear forces
-
$\begin{aligned} & \quad . \quad F_{\text {nuclear }}>F_{\text {electro }}>F_{\text {gravitation }} \\ & F_e / F_g=10^{43} \\ & \text { Therefore, } F_e \gg F_g\end{aligned}$
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"