Spermatogenesis MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Spermatogenesis is considered one the most difficult concept.
-
26 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Which of the following is male germ cell?
Directions: In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of reason (R).
Assertion – Spermiation is the transformation of spermatids into sperm.
Reason – During spermiation, sperm get nutrition from Sertoli cells.
Mark the correct choice as:
Which one of the following statements is false concerning the viability of mammalian sperm?
NEET 2026: Application Form Link | Exam Centres List | How to Fill Form
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
The correct sequence of spermatogenesis stages leading to the formation of sperm in a mature human testis is:
The difference between spermiogenesis and spermiation is
Concepts Covered - 1
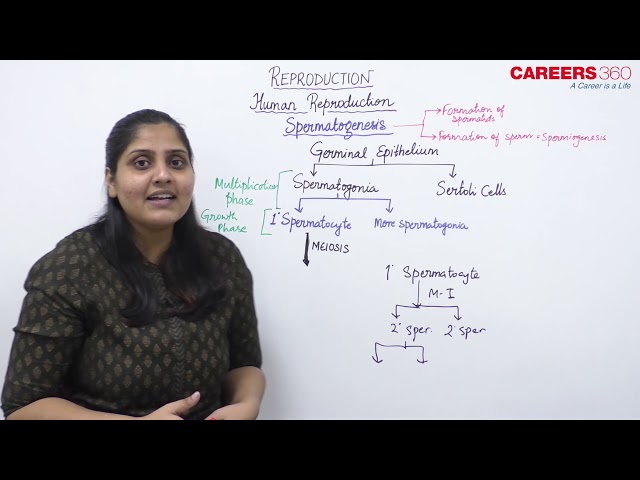
- Spermatogenesis is the process of formation of the sperms.
- It occurs in the wall of the seminiferous tubules.
- Spermatogenesis can be divided into two broad stages:
- Formation of spermatids
- Formation of sperm (spermiogenesis)
Formation of spermatids:
- The male germinal cells which produce the sperms are known as the primary germinal cells or primordial cells.
- The primordial cells pass through the following three phases for the formation of spermatids:
- The Multiplication Phase: The undifferentiated germ cells or primordial cells contain large-sized and chromatin rich nuclei. These cells multiply by repeated mitotic divisions and produce the cells which are known as the spermatogonia. Each spermatogonium is diploid and contains 2n number of chromosomes.
- The Growth Phase: In the growth phase, the spermatogonial cells accumulate a large amount of nutrition and chromatin material. Now each spermatogonial cell is known as the primary spermatocyte.
- The Maturation Phase: The primary spermatocytes are ready for first meiotic or maturation division through which two secondary spermatocytes are formed. Each secondary spermatocyte is haploid and contains n number of chromosomes. Each secondary spermatocyte passes through the second maturation or second meiotic division and produces two spermatids.
- Thus, by a meiotic or maturation division, a diploid spermatogonium produces four haploid spermatids.
- These spermatids cannot act directly as the gametes so they have to pass through the next phase, the spermiogenesis.
Formation of Sperms (Spermiogenesis):
- The metamorphosis or differentiation of the spermatids into sperm is known as spermiogenesis.
- The nucleus loses water from the nuclear sap, shrinks and assumes different shapes in different animals. The sperm nucleus in man and bull becomes ovoid and laterally flattened.
- The acrosome occurs at the anterior side of the sperm nucleus and contains proteases enzymes which help it in the easy penetration inside the egg.
- The acrosome is formed by the Golgi apparatus.
- The two centrioles of the spermatids become arranged one after the other behind the nucleus.
- The anterior one is known as the proximal centriole and posterior one is known as the distal centriole.
- The distal centriole changes into the basal bodies and gives rise to the axial filament of the sperm.

Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"