Buffer Solution NEET MCQ - NEET Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Calculating pH of a Buffer Solution(acidic), Calculating pH of a Buffer Solution(acidic), Working of Acidic Buffer, Basic Buffers is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
38 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Which one of the following pairs of solution is not an acidic buffer?
Concepts Covered - 7
A solution whose pH does not change very much when H+(H3O+) or OH- are added to it is referred to as a buffer solution.
A buffer solution is prepared by mixing a weak and its salt having common anion(i.e HA + HB forms an acidic buffer) or a weak base and its salt having common cation(i.e BOH + BA forms a basic buffer).
It can be prepared to have a desired value of pH by controlling the amounts of acids and their salts in case of acidic buffer and of bases and their salts in basic buffer.
Consider an acidic buffer containing an acid HA and say common ions A-. Now any H+ added to this solution within certain limits are neutralized by A- ions as:
While the addition of OH- ions externally (within certain limits) are neutralised by acid HA as:
Hence in both the cases, effect of addition of H+ or OH- is almost compensated for (i.e. pH almost remains constant).
Such a system (may be acidic or basic) finds enormous use not only in industrial processes but also most importantly in biological reactions. Like the pH of normal blood is 7.4 and for good health and even for the survival, it should not change below 7.1 or greater than 7.7, the body maintains it through a buffer system made of carbonate and bicarbonate ions and H2PO4- and HPO42-. Similarly, the pH of gastric juice is kept constant in order to operate good digestive functions.
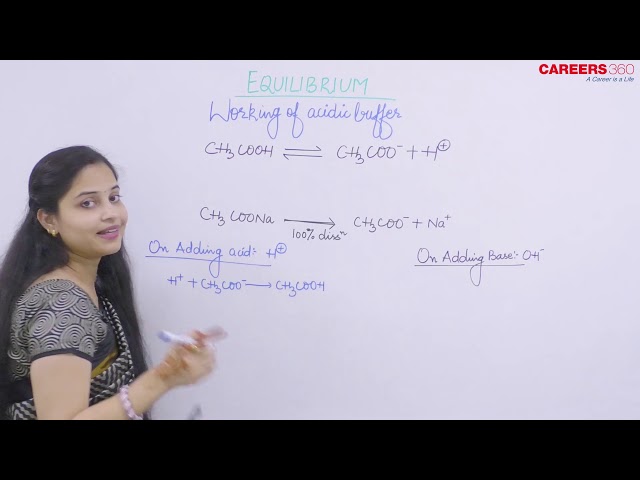
Acidic buffer solutions are the solutions that are made from a weak acid and one of its salt mainly sodium salt.
Weak Acid: CH3COOH
Salt: CH3COONa
The chemical reaction for CH3COOH and CH3COONa are as follows:
Because of common ion effect, dissociation of CH3COOH would be negligible.
Thus, the equilibrium equation for the given system can be calculated using the following equation:
This equation is also known as the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
Some examples
- Find the pH of a solution having 0.1M CH3COOH(Ka = 10-5) and 0.2M CH3COONa.
We know that pH of a solution is given as:
- Find the pH of a solution containing 0.25 moles of HCN(Ka = 10-5) and 0.10 moles of NaCN present in 1 litre solution.
We know that pH of a solution is given as:
Acidic buffer solutions are the solutions that are made from a weak acid and one of its salt mainly sodium salt.
- On addition of acid
Although on addition of acid concentration of CH3COOH increases so it wants to go in forward direction but due to common ion effect CH3COOH cannot dissociate back.
CH3COO- concentration decreases but we have abundant amount of CH3COO-. So decrease is negligible.
- On addition of base
In this case, [H+] concentration decreases and CH3COOH goes in forward direction to dissociate into H+ so as to restore the concentration of [H+]
The property of a buffer solution to resist a change in pH is known as buffer capacity. It is defined as the number of moles of acids or bases added in one litre of solution to change the pH by unity, i.e. Thus, buffer capacity is given as:
Note: The greater is the buffer capacity, the greater is its capacity to resist change in pH
Salient Features of Buffer Solutions
- It has definite pH.
- ITs pH does not change on standing.
- Its pH does not change on dilution.
- Its pH does not change significantly on the addition of small amount of acid or base.
- The pH of the buffer solution depends upon pKa and on the relative molar amount of weak acid and its conjugate base.
- Buffer solutions are used in:
- Qualitative analysis of mixture, for example, removal of phosphate.
- Quantitative analysis of estimations.
- Industrial processes such as manufacture of paper, dyes, inks, paints, drugs, etc.
- Digestion of food.
- Preservation of foods and fruits.
- Agriculture and dairy products preservations.
Basic buffer solution contains equimolar quantities of a weak base and its salt with strong acid. Some simplest basic buffers are:
- NH4OH + NH4Cl
- NH4OH + (NH4)2SO4
- CH3-NH2 + [CH3-NH3+]Cl-
The pH of the basic buffer is given as:
We already know that pH = 14 - pOH. Thus can be calculated using this equation.
For example: basic buffer we have:
In this system:
- [NH4OH]: Initial concentration of [NH4OH] is taken as at equilibrium negligible dissociation of NH4OH is there because of common-ion effect.
- [NH4+]: The concentration of NH4OH is mostly from 100% dissociation of NH4Cl.
Again, as we know:
Basic buffer solution contains equimolar quantities of a weak base and its salt with strong acid. For example: ammonium hydroxide i.e. NH4OH and ammonium chloride i.e NH4Cl.
On Adding Acid: H+ release and combines with OH- of base.
On Adding Base: OH- releases and combines with NH4+ of salt.
- On adding acid to the basic buffer, its H+ ions react with OH- ions of the base and forms H2O. Thus, in this case, solution feels that its [OH-] has decreased, thus to neutralize this effect, NH4OH dissociate in small amounts and gives [OH-] so as to restore concentration of [OH-]
- On adding base to the basic buffer, its [OH-] ions react with NH4+ ions and forms NH4OH. In this case, the solution feels that its NH4OH concentration is increased. Thus, in this case, the reaction will not proceed forward because of common ion effect.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"