- Engineering and Architecture
- Management and Business Administration
- Medicine and Allied Sciences
- Law
- Animation and Design
- Media, Mass Communication and Journalism
- Finance & Accounts
- Computer Application and IT
- Pharmacy
- Hospitality and Tourism
- Competition
- School
- Study Abroad
- Arts, Commerce & Sciences
- Learn
- Online Courses and Certifications
- Home
- Study Material
- Cymose Inflorescence and Its Types MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Cymose Inflorescence and Its Types is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
6 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
The zig-zag pattern of monochasium is seen in
Cymose inflorescence is present in:
In _________ , Peduncle ending in a flower producing lateral branch at a time ending in flower. It can be helicoid and Scar poid cyme.
The lateral branch is developed on one side, and the other branch will develop opposite to the first one in
Concepts Covered - 1
Cymose Inflorescence and Its Types
Cymose Inflorescence:
- This type of inflorescence is also known as determinate or definite inflorescence.
- Each peduncle or axis, whether main or axillary terminates into a flower.
- Younger flowers arise from the base of the older ones.
- Hence, the arrangement of flowers is in basipetal succession, that is, the older ones appear at the top and the younger ones at the base.
1. Solitary Cymose:
- It is the most simple type of inflorescence.
- The main axis does not branch and always ends in a single flower.
- For example, China Rose, Hibiscus, etc.
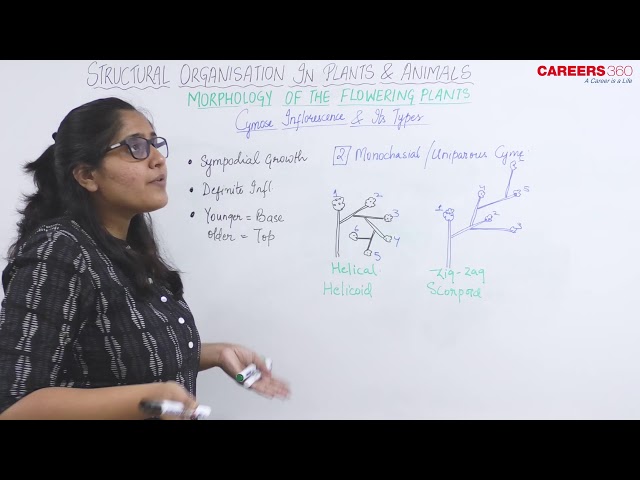
2. Uniparous / Monochasial Cyme:
- Main axis terminates into a flower.
- The lateral branch arise at the base of the terminal flower and acts as main axis.
- It also terminates into the flower.
- Monochasial cyme is of two types:
- Helicoid Monochasial Cyme: successive branching occurs at the same side such that the inflorescence acquires helical shape, e.g., Begonia, Drocera, etc.
- Scorpioid Monochasial Cyme: successive branching occurs on both sides in zig-zag or alternate manner, e.g., Ranunculus.

3. Dichasial / Biparous Cyme:
- The main axis terminates into a flower.
- Two new lateral branches arise from the base of the older one.
- These also end in flowers.
- The older flower appears in the centre while the younger flowers are towards the periphery. This type of arrangement in called centrifugal succession.
- For example, Bougainvillea, Dianthus

3. Polychasial / Multiparous Cyme:
- The main axis terminates into a flower.
- Many new flowers arise at the base of the older flower.
- For example, calotropis

4. Cymose Head:
- The peduncle is flattened.
- Many sessile and centrifugally arranged flowers are seen around the peduncle.
- The difference between racemose head and the cymose head inflorescence is of the arrangement of florets.
- The arrangement is centripetal in the racemose head while it is centrifugal in the cymose head.
- For example, Acacia
Study other Related Concepts
Cymose Inflorescence and Its Types Current Topic
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"

Get Answer to all your questions
Explore on Careers360
JEE Main
RPVT
Colleges By Branches
Colleges By Exam
Colleges By Branch
Colleges By Exams
Colleges By Ownership
Colleges By State
Colleges By Exams
Colleges By Degree
Colleges by State
Colleges by City
Colleges by State
Universities by Branches
By State
Colleges by City
Colleges by State
By State
BE/B.Tech
Diploma
MBA Specialization Colleges
Student Community: Where Questions Find Answers