Mendelian Genetics MCQ - NEET Practice Questions with Answers
Edited By admin | Updated on Sep 18, 2023 18:34 AM | #NEET
Quick Facts
-
Gregor Johann Mendel- Father of Genetics is considered one the most difficult concept.
-
39 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
- The graphical representation to calculate the probability of all possible genotypes of offspring in a genetic cross is called Punnett Square
- Given by C. Punnett
Alleles are:
What was Gregor Mendel's main contribution to science?
NEET 2026: Application Form Link | Exam Centres List | How to Fill Form
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
Hybridisation defined as:
Which one of those given below is the period for Mendel's hybridization experiments?
In his classic experiments on pea plants, Mendel did not use:
Concepts Covered - 2
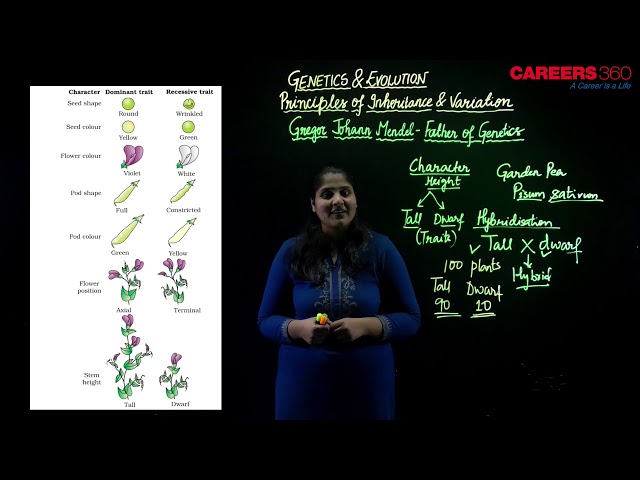
Gregor Johann Mendel- Father of Genetics
- Mendel was born in 1822 in today’s Czech Republic.
- In 1856, he began a decade-long research pursuit involving inheritance patterns in honeybees and plants, ultimately settling on pea plants as his primary model system.
- In 1865, Mendel presented the results of his experiments with nearly 30,000 pea plants to the local Natural History Society.
- In 1866, he published his work, Experiments in Plant Hybridization, in the proceedings of the Natural History Society of Brünn.
- He used garden pea (Pisum sativum) as experimental material because of its following features:
- Well-defined contrasting characters
- Bisexual flowers
- Naturally self-fertilizes, resulting in highly inbred, or “true-breeding,” pea plants
- Annual
- Large quantities of garden peas could be cultivated simultaneously.
- Mendel conducted such artificial pollination/cross-pollination experiments using several true-breeding pea lines.
- A true- breeding line is one that, having undergone continuous self-pollination, shows the stable trait inheritance and expression for several generations.
- Mendel selected 14 true-breeding pea plant varieties, as pairs which were similar except for one character with contrasting traits.
- Some of the contrasting traits selected were smooth or wrinkled seeds, yellow or green seeds, smooth or inflated pods, green or yellow pods and tall or dwarf plants
- The seven contrasting pairs of garden pea selected by Mendel were:
- Mendel succeeded in deducing the inheritance patterns of different characters as he focused on one character at a time.
- Mendel provided statistical analysis of the results which added to the credibility of data collection.
- For several reasons, Mendel’s work remained unrecognised until 1900 because of the following reasons:
- Firstly, communication was not easy (as it is now) in those days and his work could not be widely publicised.
- Secondly, the scientific community believed incorrectly, that the process of inheritance involved a blending of parental traits that produced an intermediate physical appearance in offspring; this hypothetical process appeared to be correct because of what we know now as a continuous variation.
- Thirdly, Mendel’s approach of using mathematics to explain biological phenomena was totally new and unacceptable to many of the biologists of his time.
- Finally, though Mendel’s work suggested that factors (genes) were discrete units, he could not provide any physical proof for the existence of factors or say what they were made of.
- In 1900, three Scientists - de Vries (of Holland), Correns (of Germany) and von Tschermak (of Austria) independently rediscovered Mendel’s results on the inheritance of characters.

Terminology of Genetics
- Gene:
- The term was given by Johansson.
- Genes are the smallest unit of heredity.
- Genes are those segments of DNA that carry specific information.
- Genes are made up of polynucleotides.
- The location of a gene on a chromosome is called locus.
- There can be many loci on one chromosome.
- Genotype:
- It refers to the genetic make-up of an organism.
- Phenotype:
- It refers to the physical appearance of an organism.
- Alleles or Allelomorph:
- The term was given by Bateson.
- Alleles are the alternate forms of a gene.
- They specify a pair of contrasting character.
- Dominant alleles are those that express themselves in the presence of recessive allele. These are represented by capital letters.
- Recessive alleles are masked when dominant alleles are present. These are represented by small letters.
- They have the capability to be replicated, expressed, or mutated.
- Homozygous:
- When both the alleles for a character are the same, the organism is said to have homozygous genotype.
- An organism can have homozygous dominant genotype when both the alleles of a gene are dominant.
- An organism can have homozygous recessive genotype when both the alleles of a gene are recessive.
- Heterozygous:
- When an organism has a dominant and a recessive allele for a particular gene, it is said to have heterozygous genotype.
- The phenotype of a heterozygous individual is similar to a homozygous dominant individual because of the expression of the dominant allele.
- Hemizygous:
- It is the condition when there is only a single allele present.
- Gametes are said to be hemizygous because they have only a single chromosome, with only a single allele for respective genes.
- Similarly, males are said to be hemizygous for the alleles present on X-chromosome because there is only a single X-chromosome present in males.
- Punnett Square:
- It was developed by R.C. Punnett.
- It is a graphical representation to calculate the probability of all possible genotypes of offspring in a genetic cross.
- Hybrid:
- A progeny resulting from a cross between two parents differing at least in a single character.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"