Phloem and its Components MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Components of Phloem - Sieve tubes and Companion Cells is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
22 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Function of companion cells is
Companion cells are closely associated with:
Function of companion cells is
NEET 2026: Application Form Link | Exam Centres List | How to Fill Form
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
Which of the following is the dead component of phloem?
Concepts Covered - 3
Complex Permanent Tissues - Phloem (Bast)
- The term ‘phloem’ was given by Nageli.
- Phloem is responsible for the transportation of food from source to sink.
- The organ where food is synthesized or stored is called the source. Leaves act as a sink for a considerable period. In some plants, the roots act as a sink during the autumn period.
- The organ where food is utilized, such as roots, flowers, fruits, branches, etc. are called sinks.
- On the basis of position, the phloem is of two types:
- External phloem: It is the usual phloem present outside the xylem.
- Internal or intraxylary phloem: It is present internal to the xylem. It is seen in the members of Apocynaceae, Asclepiadaceae, Convolvulaceae, Solanaceae.
- Induced or Interxylary phloem: It is the secondary phloem that occurs in patches within the secondary xylem. For example, Leptadaenia, Salvadora, Chenopodium, Boerhaavia, Amaranthus.
- On the basis of origin, phloem is of two types:
- Primary phloem: It develops from the procambium during primary growth. In some plants, it shows differentiation into protophloem (sieve elements and parenchyma) and metaphloem (sieve elements, parenchyma, and fiber) that develops later.
- Secondary Phloem: It develops from the vascular cambium during secondary growth. It is made up of the following types of cells:
- Sieve tube elements
- Companion cells
- Phloem parenchyma
- Phloem fibres or bast fibres
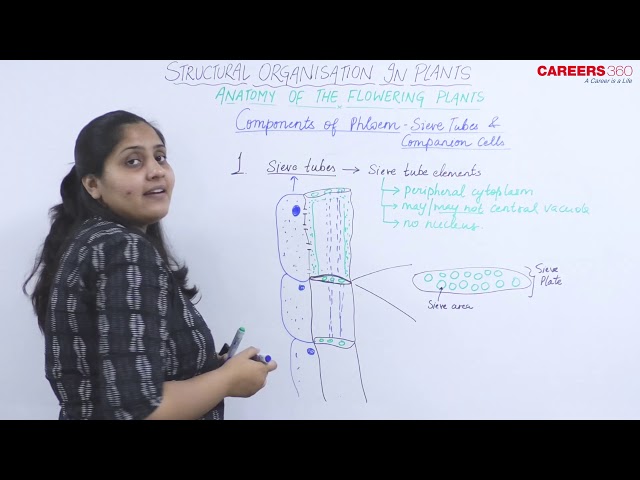
Components of Phloem - Sieve tubes and Companion Cells
- Sieve tubes are long channels made up of sieve tube elements or sieve-tube members.
- Sieve tube elements are long tube-like structures that are arranged longitudinally.
- Sieve tube elements are associated with the companion cells.
- The end walls of the sieve tube elements are perforated in a sieve-like manner. This forms the sieve area.
- A mature sieve-tube element possesses a peripheral cytoplasm and lacks a nucleus, vacuole, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, etc.
- Therefore, the metabolic activities of the sieve-tube elements are controlled by the nucleus of the companion cell.
- Companion Cells are the specialized parenchymatous cells that are closely associated with the sieve-tube elements.
- The companion cell is associated with the sieve tube element through pit fields that are present between their common walls.
- Gymnosperms have sieve cells and albuminous cells instead of sieve tube elements and companion cells.
- Sieve cells are less specialised than sieve tube elements. These are narrow elongated cells without a sieve area.
- Sieve cells are analogous to tracheids.
TIP:
- The end wall of sieve tube elements having a sieve area is called a sieve plate.
- If a sieve plate has one sieve area, it is called a simple sieve plate.
- If a sieve plate has several sieve areas, it is called a compound sieve plate.
- Each sieve pore has a single strand of cytoplasm that extends through it to the adjoining sieve pore of the sieve tube element.
- Cytoplasm and cell sap of sieve tube element are called mycoplasma.
- It is homogenous sap.
Functions of sieve tubes:
- Transfer of food in the form of organic solutes from source to sink. These regulate bidirectional flow.
- Transfer of plant hormones.

Components of Phloem - Phloem Fibres and Phloem Parenchyma
Phloem Fibres:
- These are also called the bast fibres.
- These are sclerenchymatous dead and elongated cells.
- These provide mechanical support.
- These are the only dead components of the complex tissue phloem.
Phloem Parenchyma:
- The parenchymatous cells associated with phloem.
- These are absent in monocots.
- These are present in pteridophytes.
- The cells are elongated with rounded ends and possess cellulosic cell walls.
- These cells are living and store food reserves in the form of starch and fats.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"