Secondary Growth in Dicot Stem MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Secondary Growth in Intrastelar Region of Dicot Stem, Secondary Growth in Intrastelar Region of Dicot Stem - Heartwood and Sapwood is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
20 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
The age of a tree can be estimated by:
Which of the following statements about cork cambium is incorrect?
Bark does not include
NEET 2026: Application Form Link | Exam Centres List | How to Fill Form
NEET Prep: Mock Test | 10 Years PYQ's | Syllabus
NEET 2026: Boards Cheat Sheet | Mind Maps & Diagrams Guide | Formula Sheet
Latest: Allied and Health Sciences | Paramedical Universities Accepting Applications
Concepts Covered - 4
Secondary Growth in Intrastelar Region of Dicot Stem
- The vascular bundles present in the Dicot stem are conjoint, collateral and open.
- That means, they have a fascicular or intrafascicular cambium present the primary xylem and primary phloem.
- The intrafascicular cambium is primary meristem having lateral position in the plant body.
- Events During the Intrastelar Secondary Growth in Dicot Stem:
Formation of Cambium Ring
- The intrafascicular cambium gets activated to perform meristematic activity.
- The parenchymatous cells of the pith rays that are present adjacent to the intrafascicular cambium dedifferentiate to become meristematic.
- The meristem so formed through the dedifferentiation of the cells of the pith rays is called secondary meristem or interfascicular meristem.
- The interfascicular meristem joins with the strip of intrafascicular meristem to form a complete cambium ring or vascular cambium.

2. Formation of Secondary Vascular Tissues
- The vascular cambium produces secondary xylem towards inside, that is, towards the pith.
- It produces secondary phloem towards the outside.
- The continuous formation of secondary xylem crushes the primary phloem. The primary xylem remains intact at some places.
- The vascular cambium also produces radial parenchymatous cells that passes through the secondary xylem and secondary phloem. These are called secondary medullary rays.
- The secondary xylem has axial and radial (horizontal) system while radial system is absent in primary xylem.
- Primary xylem has long vessels and tracheids as compared to secondary xylem.

Secondary Growth in Intrastelar Region of Dicot Stem - Annual Rings
- The activity of the cambium is markedly affected by environmental fluctuations.
- In temperate regions, these fluctuations have a great role in defining the activity of the cambium.
- During the spring season, the activity of thee cambium increases.
- It produces a large number of xylary elements with wider lumen.
- The wood formed during this season is called spring wood or early wood.
- During the autumn season, the activity of cambium reduces.
- It produces narrow vessels in secondary xylem. A large amount of xylem fibres are produced.
- The wood formed during the autumn season is called autumn wood or late wood.
- The early wood and late wood occur in the form of two concentric rings, forming a single annual ring.
- An annual ring is called so because it is produced in a span of a year.
- The annual rings reflect the age of trees.
- Determination of age of tree by counting the annual rings in called dendrochronology.
- The activity of cambium is also affected by disease, drought, defoliation, etc. In such conditions false rings can be observed.
- In tropical trees, there is no annual rings formation because of uniformity in climate.
- In roots, the annual rings are not visible because inside the soil the temperature remains constant throughout the year.
- The roots of Salix are an exception because the annual rings are visible in them.

Secondary Growth in Intrastelar Region of Dicot Stem - Heartwood and Sapwood
- When a transverse section of a woody trunk is taken, two regions are distinctly visible.
- In the centre, there is dark coloured wood called heartwood.
- Heartwood is made up of dead and non-functional components of wood.
- Heartwood is also called duramen.
- The lumen of vessels in the heartwood has been blocked by tyloses.
- Tyloses are balloon-like structures formed due to protrusion of xylem parenchyma cells into the lumen of vessels.
- These parenchyma cells become lignified and dead, thereby making the vessels non-functional.
- In the tracheids of gymnosperms, the tylosoids are present.
- The heartwood is durable and resistant to parasitic and microbial attack.
- It gives mechanical support to the tree trunk.
- It appears dark due to deposition of organic compounds like tannins, resins, oils, gums, aromatic substances and essential oils.
- In the periphery of the tree trunk, surrounding the heartwood, there is lighter colored wood made up of functional xylem elements.
- This is called sapwood. It is involved in the conduction of sap.
- Sapwood is also called alburnum.

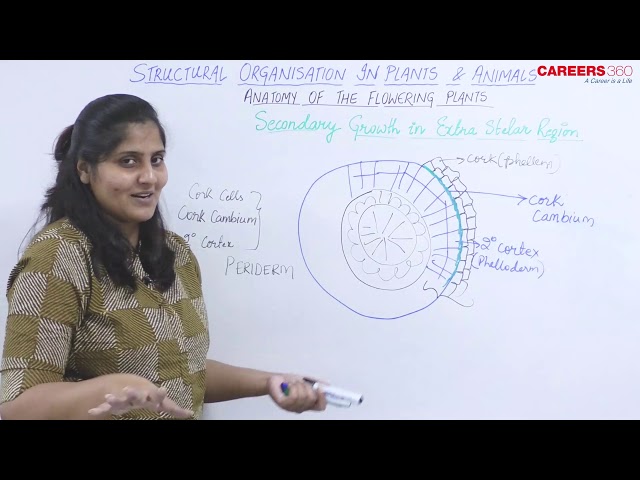
Secondary Growth in Extra Stelar Region
- The continuous secondary growth in the intrastelar region adds more and more secondary xylem and secondary phloem.
- This exerts pressure on the tissues lying towards the outer side, that is, cortex and epidermis.
- The epidermis ruptures due to the exertion of the pressure and the underlying tissues are exposed to the environment.
- At this stage, a secondary tissue called periderm develops.
- Periderm develops through the activity of cork cambium or phellogen.
- Cork cambium or phellogen is the secondary meristem that develops generally from the collenchymatous cells of hypodermis, sometimes from the cells of the epidermis (apple), pericycle (Cimatis), phloem (vitis).
- Phellogen gives rise to cork or phellem on the outer side and secondary cortex of phelloderm on the inner side.
- Phellem or cork is the dead tissue with suberised cell walls. It is impermeable to water and is used commercially.
- Quercus suber is commercial cork.
- Secondary cortex or phelloderm is living tissue. It stores food and replaces the damaged primary cortex.
- Phellem, phellogen and phelloderm are called periderm.
- Periderm and fragments of epidermis form the protective tissues in an old dicot stem.
Bark:
- This term is used to refer to all the tissues outside the vascular cambium.
- It includes secondary phloem, periderm and epidermis.
- Removal of bark , called the ringing experiment, causes serious injury to the plant because it removes the secondary phloem which restricts the conduction of food.
- Roots die first in the ringing experiment.
Rhytidome:
- All the tissues outside the cork cambium is called rhytidome
- It consists of cork and epidermis.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"