Classification Of Lipids MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
20 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
A typical fat molecule is made up of:
Concepts Covered - 2
TYPES OF LIPIDS - Simple Lipids

Simple Lipids: These are esters of fatty acids and are linked with various alcohols. These are of following types:
1) Fats and Oils:
- These are esters of fatty acids and glycerol.
- Fat is solid at room temperature.
- Glycerol is an organic compound (alcohol) with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (OH) groups.
- In a fat molecule, the fatty acids are attached to each of the three carbons of the glycerol molecule with an ester bond through an oxygen atom.
- Fats are also called triacylglycerols or triglycerides because of their chemical structure.

- When fats are rich in unsaturated fatty acids, they are called oils.
- They are liquid at room temperature.
- If there is one double bond in the molecule, then it is known as monounsaturated fat (e.g., olive oil).
- If there is more than one double bond, then it is known as a polyunsaturated fat (e.g., canola oil).
- Triglycerides are abundant and constitute about 98 per cent of all dietary lipids.
- Oils are recommended by physicians owing to their unsaturated nature.
- Many vitamins are fat-soluble, and fats serve as a long-term storage form of fatty acids: a source of energy.
- They also provide insulation for the body.
2). Waxes:
- Waxes are made up of long fatty acid chains esterified to long-chain alcohols other than glycerols.
- Waxes are produced naturally by skin glands as a protection, to keep it lubricated, pliable, and water-proof.
- Wax also covers hair, feathers, and wool.
- Because of the hydrophobic nature of waxes, they prevent water from sticking on the surface of leaves.
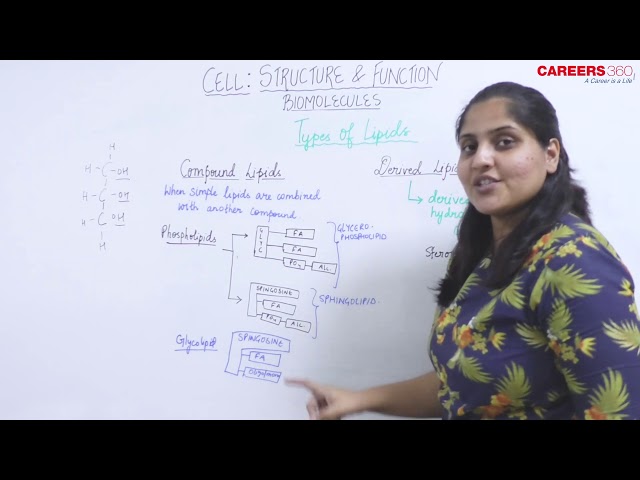
Types of Lipids - Compound Lipids and Derived Lipids
Compound Lipids: These are formed when the simple lipids combine with another compound. These are of following types:
a) Phospholipids: These contain:
- A platform molecule (glycerol or sphingosine)
- One or more fatty acids
- A phosphate group
- An alcohol component
- The fatty acids give the hydrophobic property while the phosphate and alcohol group give hydrophilic property.
Hence, phospholipids are amphipathic.


b) Glycolipids: These are formed when carbohydrates combine with lipids. Because of presence of sphingosine, they are also called sphingolipids.

Derived Lipids:
- These substances are derived by hydrolysis from compound and simple lipids.
- Steroids: These are composed of fused hydrocarbon rings and a long hydrocarbon chain.
- Cholesterol is the most common type of steroid. It is composed of four fused hydrocarbon rings and one end of this ring contains a hydrocarbon chain while the other end has an -OH group.
- Bile salts are modified cholesterol needed for digestion of fats.

Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"