Different Phases of Meiosis I MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Quick Facts
-
Stages of Meiosis Ⅰ - Prophase I, Stages of Meiosis Ⅰ - Metaphase I and Anaphase I is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
74 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
During Meiosis 1, in which stage synapsis takes place?
Match the stages of meiosis in Column I to their characteristic feature in Column II and select the correct option using the codes given below:
| Column I | Column II |
|
a. Pachytene |
(i) Paring of homologous chromosomes |
|
b. Metaphase I |
(ii) Terminalization of chiasmata |
|
c. Diakinesis |
(iii) Crossing-over takes place |
| d. Zygotene |
(iv) Chromosomes align at the equatorial plate |
Codes :
A b c d
The complex formed by a pair of synapsed homologous chromosomes is called:
The enzyme recombinase is required at which stage of meiosis:
During mitosis ER and the nucleolus begin to disappear at:
Concepts Covered - 3
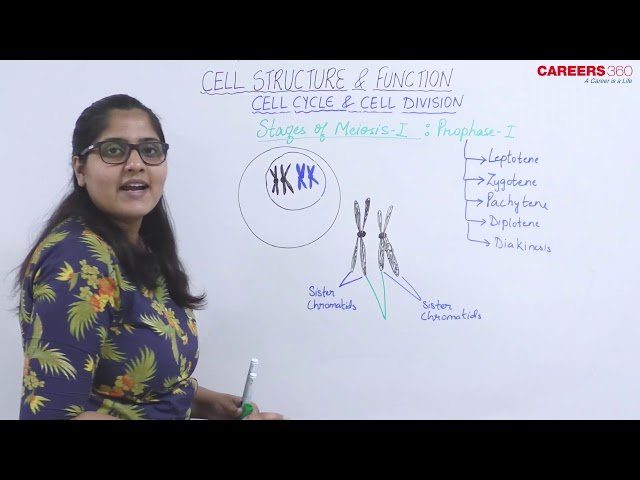
Stages of Meiosis Ⅰ - Prophase I
- In meiosis I, the actual reduction in the number of chromosomes occurs.
- It starts after the homologous chromosomes have replicated during S-phase and the proteins required for division have been synthesized in G2 phase.
- Therefore, it occurs after the interphase of cell cycle.
- It is studied under Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I and Telophase I.
Prophase I
- It is the longest phase of meiosis I.
- It is divided into five substages: leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene and diakinesis.
LEPTOTENE:
- The chromatin begins to condense to form chromosomes.
- Chromosomes appear as thin and long threads.
- By the end of this phase, chromosomes become visible under microscope.
ZYGOTENE:
- The pairing of the homologous chromosomes initiate in this phase.
- The pairing of homologous chromosomes is called synapsis.
- The synapsed homologous chromosomes appear in the form of bivalent of chromosomes or tetrad of chromatids.
- In the tetrad, two similar chromatids of the same chromosome are called sister chromatids and those of two homologous chromosomes are termed non-sister chromatids.
- A filamentous ladder like nucleoproteins complex, called synaptonemal complex appears between the homologous chromosomes. It holds the homologous chromosomes together.
PACHYTENE:
- The exchange of parts between non-sister chromatids occurs during this phase.
- It is called the crossing over.
- Crossing over occurs through breakage and reunion of chromatids segments.
- Breakage is called nicking. It is assisted by an enzyme endonuclease.
- Reunion termed annealing. It is aided by an enzyme ligase.
DIPLOTENE:
- This phase involves pulling away of the synapsed homologous chromosomes.
- The point of attachment of the homologous chromosomes where crossing over occurred is called chiasma.
- Homologous chromosomes remain attached only at chiasma.
- There can be more than one chiasmata.
DIAKINESIS:
- It marks the terminalization of chiasma.
- Nuclear membrane and nucleolus degenerates.
- Chromosome recondense and tetrad moves to the metaphase plate.
- Spindle fibres begin to form.
- When the diakinesis of prophase-I is completed than cell enters into the metaphase-I.

Stages of Meiosis Ⅰ - Metaphase I and Anaphase I
Metaphase I
- During this phase, bivalents arrange themselves on the metaphase plate.
- Hence, a fully formed spindle and equatorial alignment of the chromosomes are seen during this phase.
- The alignment of homologous chromosomes is independent of each other.
- This is responsible for generating genetic variability.
Anaphase I
- The homologous chromosomes of each bivalent separate from each other.
- The separated homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles
- Therefore, in this phase, the chromosomes separate and not the chromatids.
- So, each chromosome will still have two sister chromatids.
- Hence, anaphase I involve a reduction in the number of chromosomes.

Homologous Chromosomes separating from each other during Anaphase I
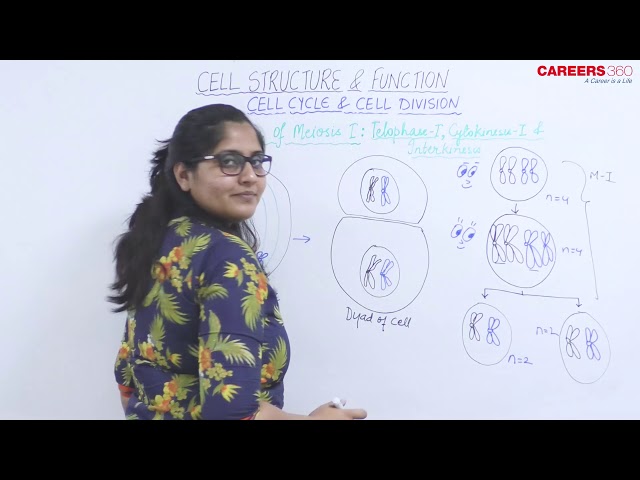
Stages of Meiosis Ⅰ - Telophase I, Cytokinesis I and Interkinesis
Telophase I
- Two daughter nuclei are formed but the chromosome number is half than the chromosome number of mother cell.
- This phase does not necessarily completes wholly.
- The spindle disappears, but new nuclear envelopes need not form before the onset of meiosis II.
Cytokinesis I
- It may or may not follow the telophase I.
- When it occurs, it forms the dyad of cells.
Interkinesis
- Following cytokinesis I, the cells enter interkinesis.
- It is also known as intermeiotic interphase.
- During this phase, there is no duplication or replication of DNA as the chromosomes are already duplicated.
Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"