Types of Enzyme Inhibition MCQ - Practice Questions with Answers
Edited By admin | Updated on Sep 18, 2023 18:34 AM | #NEET
Quick Facts
-
Enzyme Inhibition is considered one of the most asked concept.
-
18 Questions around this concept.
Solve by difficulty
Competitive inhibition could be reversed by increasing the concentration of
Concepts Covered - 1
Enzyme Inhibition
Enzyme Inhibition
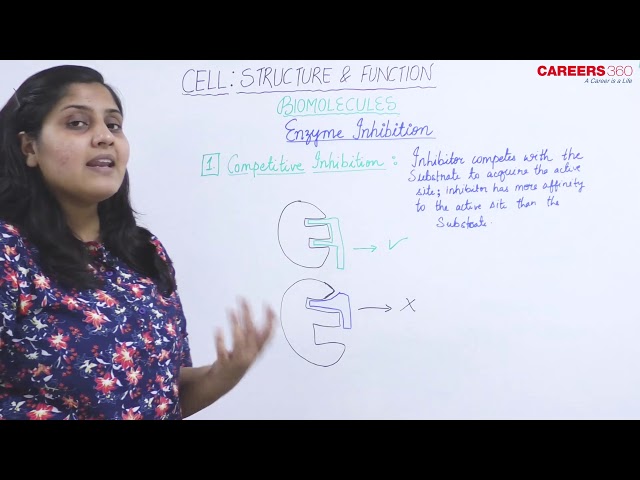
Competitive Inhibition:
- It occurs when an inhibitor molecule binds to the active site of the enzyme.
- An inhibitor molecule is similar enough to the substrate.
- It is called competitive inhibition because an inhibitor competes with the substrate for the active binding site.
- Competitive inhibitors have a much higher affinity for the active site than the natural substrate.
- Competitive inhibitors can only bind to E and not to ES.
- They increase Km by interfering with the binding of the substrate, but they do not affect Vmax because the inhibitor does not change the catalysis in ES because it cannot bind to ES.
- It can be overcome by increasing the concentration of the substrate.
- An example of a use for a competitive inhibitor is in the treatment of influenza via the neuraminidase inhibitor, Relenza
Uncompetitive Inhibition:
- Sometimes, the binding of the substrate to the active site changes the conformation of the enzyme.
- This creates an allosteric site which was not present prior to the binding of the substrate.
- An inhibitor can bind to this site and cause inhibition.
- It cannot be overcome by increasing substrate concentration.
Non-Competitive Inhibition:
- Some enzymes have permanent allosteric sites that can bind the inhibitor.
- As the inhibitor does not compete for the active site, it is called non-competitive inhibition.
- It is also called allosteric inhibition.
- In non-competitive inhibition, the Km does not change. This
- is because Km is a measure of the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate and this can only be measured by the active enzyme.
- The fixed amount of inactive enzyme in non-competitive inhibition does not affect the Km and the Km, therefore is unchanged.
- An example of a use for a noncompetitive inhibitor is in the use of cyanide as a poison (prevents aerobic respiration)


Study it with Videos
"Stay in the loop. Receive exam news, study resources, and expert advice!"